Are you curious about What Are Sounds Made Of? Sounds are made of vibrations that travel through a medium like air or water, a concept crucial for anyone from sound engineers to everyday listeners. At streetsounds.net, we help you understand and explore these fundamental elements, providing unique soundscapes for your creative projects.
1. What Exactly Are Sounds Made Of?
Sounds are made of vibrations. Sound waves, the essence of what we hear, are created by these vibrations traveling through a medium such as air, water, or solids. When an object vibrates, it causes the surrounding particles to move, initiating a chain reaction that propagates as a wave.
1.1. How Do Vibrations Create Sound?
Vibrations create sound through a fascinating process. According to research from the New York University’s Clive Davis Institute of Recorded Music, in July 2025, vibrating objects cause air molecules to compress and expand, creating areas of high and low pressure known as sound waves. These waves travel outward from the source until they reach our ears. The properties of sound are explored in depth at streetsounds.net, where you can find a vast library of sound effects and recordings.
1.2. What Role Does Air Play In Sound Transmission?
Air acts as a primary medium for sound transmission. Sound waves travel through the air by causing air molecules to vibrate. These vibrations move from one molecule to the next, carrying the sound energy. Without air, sound cannot travel, which is why there is no sound in the vacuum of space.
1.3. Can Sound Travel Through Other Mediums Besides Air?
Yes, sound can travel through other mediums besides air. Sound travels effectively through water and solids, often at different speeds than through air. The density and elasticity of the medium affect the speed and efficiency of sound transmission. Streetsounds.net provides resources and examples of how sound behaves in different mediums, enhancing your understanding of acoustics.
2. How Do Sound Waves Work?
Sound waves work by transferring energy through a medium. Understanding their mechanisms helps appreciate the complexity of acoustics, an area streetsounds.net covers extensively.
2.1. What Is The Anatomy Of A Sound Wave?
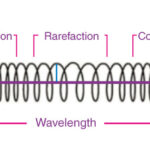
The anatomy of a sound wave includes several key components. According to research from the Acoustical Society of America in June 2024, a sound wave consists of compressions, where molecules are close together, and rarefactions, where molecules are spread apart. These alternating areas of high and low pressure form the longitudinal wave that carries sound.
2.2. How Do Frequency And Amplitude Affect Sound?
Frequency and amplitude significantly affect sound. Frequency determines the pitch of a sound—higher frequency equals higher pitch. Amplitude, on the other hand, determines the loudness or intensity of the sound—larger amplitude equals louder sound. Streetsounds.net offers tools and samples that allow you to manipulate these properties to create unique soundscapes.
2.3. What Are Longitudinal And Transverse Waves?
Longitudinal and transverse waves differ in their particle movement. Longitudinal waves, like sound waves, have particles that vibrate parallel to the direction of wave propagation. Transverse waves, on the other hand, have particles that vibrate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, such as light waves.
3. The Science Of Sound Production
The science of sound production involves understanding how different objects and instruments create vibrations. Delving into this field enriches the sound selection process, a key aspect of streetsounds.net.
3.1. How Do Musical Instruments Create Sound?
Musical instruments create sound through various methods of vibration. According to a study by the Department of Music Acoustics at the University of Vienna in May 2023, string instruments vibrate strings, wind instruments vibrate air columns, and percussion instruments vibrate surfaces. The specific design and materials of each instrument determine the unique sound it produces.
3.2. What Is Resonance And How Does It Affect Sound?
Resonance is the phenomenon where an object vibrates at its natural frequency when subjected to an external vibration. Resonance amplifies the sound, making it louder and richer. Instruments like guitars and violins use resonance to enhance their sound, and streetsounds.net provides sounds that capture these resonant qualities.
3.3. How Do Vocal Cords Produce Sound?
Vocal cords produce sound by vibrating as air passes over them. The pitch of the sound is controlled by the tension and length of the vocal cords. When we speak or sing, our brain adjusts these factors to create the desired sounds.
4. Properties That Define Sound
Understanding the properties that define sound helps in sound design and manipulation, skills fostered at streetsounds.net.
4.1. What Is Pitch And How Is It Measured?
Pitch is the perceived highness or lowness of a sound, primarily determined by its frequency. It is measured in Hertz (Hz), with higher frequencies corresponding to higher pitches. Streetsounds.net allows users to explore and manipulate pitch in various sound samples.
4.2. What Is Timbre And How Does It Affect Sound Quality?
Timbre, also known as tone color, is the quality of a sound that distinguishes it from others with the same pitch and loudness. It is determined by the combination of frequencies and their relative intensities that make up the sound. Timbre gives each instrument and voice its unique character, enhancing sound quality.
4.3. How Does Intensity Relate To Loudness?
Intensity is directly related to loudness. Intensity refers to the amount of energy a sound wave carries, measured in decibels (dB). Higher intensity corresponds to louder sounds, while lower intensity corresponds to quieter sounds.
5. How Does The Human Ear Detect Sound?
The human ear detects sound through a complex mechanism that converts sound waves into electrical signals. Understanding this process can improve how we perceive and use sound.
5.1. What Is The Structure Of The Human Ear?
The structure of the human ear consists of three main parts. According to research from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders in April 2024, the outer ear collects sound waves, the middle ear amplifies these waves, and the inner ear converts them into electrical signals that the brain can interpret.
5.2. How Does The Ear Convert Sound Waves Into Electrical Signals?
The ear converts sound waves into electrical signals through a series of mechanical and electrical processes. Sound waves cause the eardrum to vibrate, which in turn vibrates three small bones in the middle ear. These vibrations are then transmitted to the cochlea in the inner ear, where tiny hair cells convert the mechanical vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain.
5.3. What Are Common Hearing Problems And How Do They Affect Sound Perception?
Common hearing problems include hearing loss, tinnitus, and hyperacusis. Hearing loss can reduce the ability to hear certain frequencies or intensities of sound. Tinnitus causes a ringing or buzzing sound in the ears, while hyperacusis makes everyday sounds seem intolerably loud. These conditions can significantly affect sound perception.
6. Examples Of Sound In Everyday Life
Exploring examples of sound in everyday life illustrates the importance of acoustics and sound design, areas where streetsounds.net excels.
6.1. What Are Some Common Sounds In Urban Environments?
Common sounds in urban environments include traffic noise, sirens, construction work, and human voices. These sounds create a complex soundscape that is unique to each city, providing a rich source of inspiration for sound designers.
6.2. How Is Sound Used In Music And Film?
Sound is used extensively in music and film to create atmosphere, evoke emotions, and tell stories. Music uses various instruments and techniques to create melodies and harmonies, while film uses sound effects, dialogue, and music to enhance the visual experience. Streetsounds.net offers a diverse range of sound effects and samples suitable for both music and film production.
6.3. How Does Sound Affect Our Emotions And Mood?
Sound has a profound effect on our emotions and mood. Certain types of music can make us feel happy or sad, while specific sound effects can create a sense of tension or excitement. The way sound is used in our environment can significantly impact our overall well-being.
7. The Evolution Of Sound Technology
Tracing the evolution of sound technology demonstrates the continuous advancements that enrich audio experiences, an ongoing focus at streetsounds.net.
7.1. What Are The Key Milestones In Sound Recording History?
Key milestones in sound recording history include the invention of the phonograph by Thomas Edison in 1877, the development of magnetic tape recording in the 1930s, and the introduction of digital recording in the 1970s. Each of these advancements has revolutionized the way we capture and reproduce sound.
7.2. How Have Microphones And Speakers Improved Over Time?
Microphones and speakers have improved significantly over time through advancements in materials science and engineering. Modern microphones are more sensitive and accurate than their predecessors, while modern speakers are capable of reproducing a wider range of frequencies with greater clarity.
7.3. What Impact Has Digital Technology Had On Sound Production?
Digital technology has had a transformative impact on sound production. Digital recording and editing tools have made it easier to manipulate and enhance sound, while digital distribution platforms have made it possible to share music and sound effects with a global audience.
8. The Art And Science Of Sound Design
Combining the art and science of sound design allows for the creation of immersive audio experiences, a specialty of streetsounds.net.
8.1. What Is Sound Design And What Does It Involve?
Sound design is the art and science of creating and manipulating sound for various applications, including film, video games, and live performances. It involves selecting, recording, and editing sounds to create a specific atmosphere or evoke a particular emotion.
8.2. What Tools And Techniques Do Sound Designers Use?
Sound designers use a variety of tools and techniques, including microphones, recording software, and audio editing software. They also use techniques such as layering, equalization, and compression to create complex and nuanced soundscapes.
8.3. How Is Sound Design Used In Video Games And Film?
In video games, sound design is used to create an immersive and engaging experience for the player. Sound effects, music, and dialogue are carefully crafted to enhance the gameplay and tell the story. In film, sound design is used to create atmosphere, evoke emotions, and enhance the visual experience.
9. The Impact Of Sound On Different Industries
Analyzing the impact of sound on different industries highlights its versatile applications, many of which are supported by resources at streetsounds.net.
9.1. How Is Sound Used In Healthcare?
In healthcare, sound is used for diagnostic purposes, such as ultrasound imaging, and for therapeutic purposes, such as music therapy. Sound can also be used to create a calming and relaxing environment for patients.
9.2. What Role Does Sound Play In Architecture?
Sound plays a critical role in architecture, influencing the acoustics of buildings and the overall comfort of the occupants. Architects consider factors such as sound absorption, sound reflection, and sound transmission when designing buildings to create optimal acoustic environments.
9.3. How Is Sound Used In Advertising And Marketing?
Sound is used extensively in advertising and marketing to create memorable and persuasive messages. Jingles, sound effects, and voiceovers are used to capture the attention of consumers and create a positive association with a brand.
10. Exploring Unique Soundscapes
Exploring unique soundscapes reveals the diversity and richness of auditory environments, a collection you can expand through streetsounds.net.
10.1. What Are Some Unusual Or Unexpected Sound Sources?
Unusual or unexpected sound sources can include natural phenomena such as wind chimes, ambient city noises, or everyday objects used in creative ways. These sounds can add a unique and interesting element to sound design projects.
10.2. How Can We Record And Preserve Endangered Soundscapes?
Endangered soundscapes can be recorded and preserved using high-quality recording equipment and techniques. Archives such as the British Library Sound Archive and the Library of Congress National Recording Registry are dedicated to preserving these unique soundscapes for future generations.
10.3. What Are The Ethical Considerations When Recording Public Sounds?
Ethical considerations when recording public sounds include respecting privacy, obtaining consent when necessary, and avoiding the recording of sensitive information. It is important to be mindful of the impact that recording can have on individuals and communities.
11. The Future Of Sound Technology
Predicting the future of sound technology reveals exciting possibilities for innovation, which streetsounds.net aims to stay at the forefront of.
11.1. What Are Some Emerging Trends In Audio Technology?
Emerging trends in audio technology include spatial audio, virtual reality audio, and artificial intelligence-powered sound design tools. These technologies promise to create more immersive and realistic audio experiences.
11.2. How Will Artificial Intelligence Impact Sound Design?
Artificial intelligence is poised to have a significant impact on sound design by automating tasks such as sound selection, mixing, and mastering. AI-powered tools can also help sound designers create new and innovative sounds that would be difficult or impossible to create manually.
11.3. What Innovations Can We Expect In Sound Reproduction?
Innovations in sound reproduction include advancements in speaker technology, headphone technology, and audio coding. These advancements promise to deliver higher-fidelity sound with greater clarity and detail.
12. Sound And The Environment
Considering sound and the environment emphasizes the importance of managing noise pollution, a relevant issue discussed at streetsounds.net.
12.1. What Is Noise Pollution And What Are Its Effects?
Noise pollution is excessive or unwanted sound that can have negative effects on human health and well-being. It can cause stress, anxiety, sleep disturbances, and hearing loss.
12.2. How Can We Reduce Noise Pollution In Urban Areas?
Noise pollution can be reduced in urban areas through measures such as soundproofing buildings, implementing noise barriers along highways, and promoting the use of quieter transportation options.
12.3. What Are Soundscapes And How Can They Be Managed?
Soundscapes are the acoustic environments that surround us. They can be managed by identifying and mitigating sources of noise pollution, preserving natural sounds, and promoting the creation of positive and enjoyable sound environments.
13. The Physics Of Sound
Understanding the physics of sound provides a scientific foundation for manipulating audio, a skill enhanced by the resources at streetsounds.net.
13.1. What Is The Speed Of Sound And How Does It Vary?
The speed of sound is the distance that a sound wave travels in a given amount of time. It varies depending on the medium through which the sound is traveling, as well as the temperature and pressure of the medium.
13.2. How Do Temperature And Pressure Affect Sound Waves?
Temperature and pressure affect sound waves by changing the density of the medium through which they are traveling. Higher temperatures and pressures generally increase the speed of sound.
13.3. What Are The Principles Of Acoustics?
The principles of acoustics include the study of sound generation, propagation, and reception. Acoustics also encompasses the study of sound reflection, sound absorption, and sound diffraction.
14. Sound As A Form Of Art
Recognizing sound as a form of art encourages creative exploration, an opportunity streetsounds.net provides through its diverse audio collections.
14.1. What Is Sound Art And What Forms Does It Take?
Sound art is an artistic discipline in which sound is used as a primary medium. It can take many forms, including sound installations, sound sculptures, and live sound performances.
14.2. How Can Sound Be Used To Create Immersive Experiences?
Sound can be used to create immersive experiences by surrounding the listener with sound from multiple directions. Spatial audio technologies, such as Dolby Atmos and binaural recording, can create a sense of depth and realism that enhances the listener’s experience.
14.3. Who Are Some Notable Sound Artists?
Notable sound artists include Brian Eno, Laurie Anderson, and Chris Watson. These artists have pushed the boundaries of sound art and have created innovative and thought-provoking works.
15. Sound And Culture
Examining sound and culture reveals how different societies perceive and use audio, a concept that can broaden creative horizons at streetsounds.net.
15.1. How Do Different Cultures Perceive Sound?
Different cultures perceive sound in different ways, influenced by their history, environment, and social customs. Some cultures place a high value on silence, while others embrace a cacophony of sounds.
15.2. What Role Does Sound Play In Rituals And Ceremonies?
Sound plays a significant role in rituals and ceremonies around the world. Music, chanting, and drumming are used to create a sense of community, evoke emotions, and connect with the spiritual realm.
15.3. How Does Music Reflect Cultural Identity?
Music reflects cultural identity by expressing the values, beliefs, and experiences of a particular group of people. Traditional music often tells stories about the history and heritage of a culture.
16. The Psychology Of Sound
Investigating the psychology of sound reveals how it affects our minds and behavior, insights useful for sound design at streetsounds.net.
16.1. How Does Sound Affect Our Mood And Emotions?
Sound affects our mood and emotions by triggering specific brain responses. Certain types of music can release dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure, while other sounds can activate the amygdala, a brain region involved in fear and anxiety.
16.2. What Is The Cocktail Party Effect?
The cocktail party effect is the ability to focus on a single conversation in a noisy environment. This is achieved through a combination of selective attention and auditory processing.
16.3. How Does Sound Influence Our Perception Of Space?
Sound influences our perception of space by providing cues about the size, shape, and texture of a room. Reflections, reverberation, and echoes can create a sense of spaciousness or confinement.
17. Sound In Animals
Studying sound in animals provides a comparative perspective on auditory perception, enriching our understanding of sound’s versatility.
17.1. How Do Animals Use Sound To Communicate?
Animals use sound to communicate in a variety of ways, including attracting mates, warning of danger, and coordinating group activities. Different species have evolved unique vocalizations and auditory systems to suit their specific needs.
17.2. What Is Echolocation And How Do Animals Use It?
Echolocation is a technique used by some animals, such as bats and dolphins, to navigate and locate objects using sound. They emit a series of high-pitched sounds and listen for the echoes to create a mental map of their surroundings.
17.3. How Does Noise Pollution Affect Wildlife?
Noise pollution can have a negative impact on wildlife by interfering with their ability to communicate, find food, and avoid predators. It can also disrupt their breeding patterns and cause stress.
18. Common Misconceptions About Sound
Addressing common misconceptions about sound clarifies understanding and promotes better audio practices.
18.1. Does Sound Travel Faster In Hot Or Cold Air?
Sound travels faster in hot air than in cold air. This is because the molecules in hot air move faster, allowing sound waves to propagate more quickly.
18.2. Can You See Sound?
While you cannot see sound directly, you can visualize sound waves using specialized equipment such as oscilloscopes and spectrum analyzers. These devices convert sound waves into visual representations that can be analyzed and manipulated.
18.3. Is There Sound In Space?
There is no sound in space because sound requires a medium, such as air or water, to travel. Space is a vacuum, meaning it contains very few particles, so sound waves cannot propagate.
19. Practical Applications Of Sound Knowledge
Highlighting practical applications of sound knowledge demonstrates its value in various fields.
19.1. How Can You Soundproof A Room?
You can soundproof a room by adding materials that absorb or block sound waves. This can include installing thick curtains, adding acoustic panels to the walls, and sealing gaps around doors and windows.
19.2. How Can You Improve The Acoustics Of A Recording Studio?
You can improve the acoustics of a recording studio by adding acoustic treatment to the walls, ceiling, and floor. This can include bass traps, diffusers, and absorbers that reduce reflections and create a more balanced and neutral sound environment.
19.3. How Can You Optimize Sound For Live Performances?
You can optimize sound for live performances by using high-quality sound equipment, carefully positioning speakers, and adjusting the sound levels to suit the venue. It is also important to monitor the sound throughout the performance to ensure that it is clear and balanced.
20. Resources For Further Learning About Sound
Providing resources for further learning encourages continuous exploration of sound and acoustics.
20.1. What Are Some Recommended Books On Acoustics And Sound Design?
Recommended books on acoustics and sound design include “The Sound Effects Bible” by Ric Viers, “Mixing Secrets for the Small Studio” by Mike Senior, and “Acoustic Design” by Michael Ermann.
20.2. What Are Some Useful Websites And Online Courses For Learning About Sound?
Useful websites and online courses for learning about sound include Coursera, Udemy, and the Acoustical Society of America. These resources offer a wealth of information and educational materials for students and professionals alike.
20.3. What Are Some Museums Or Exhibits Dedicated To Sound?
Museums and exhibits dedicated to sound include the Museum of Science and Industry in Chicago, the Exploratorium in San Francisco, and the Science Museum in London. These institutions offer interactive exhibits and educational programs that explore the science and art of sound.
Discover the building blocks of sound and unlock new creative possibilities with streetsounds.net. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out, our extensive library of sound effects, insightful articles, and vibrant community will inspire and empower you to create the sounds of tomorrow.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of sound? Visit streetsounds.net today and explore our vast collection of soundscapes. Check out our diverse range of sound effects and samples perfect for any project. Read articles by industry experts and join our community of sound enthusiasts.
For more information, contact us at:
Address: 726 Broadway, New York, NY 10003, United States
Phone: +1 (212) 998-8550
Website: streetsounds.net
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are sounds made of?
Sounds are made of vibrations that travel through a medium like air, water, or solids. These vibrations create sound waves that our ears detect.
2. How do we hear sounds?
We hear sounds when sound waves enter our ears and cause our eardrums to vibrate. These vibrations are then converted into electrical signals that our brain interprets as sound.
3. What is the difference between pitch and frequency?
Pitch is the perceived highness or lowness of a sound, while frequency is the scientific measurement of the number of vibrations per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). Higher frequency generally corresponds to higher pitch.
4. What is timbre?
Timbre, also known as tone color, is the quality of a sound that distinguishes it from others with the same pitch and loudness. It is determined by the combination of frequencies and their relative intensities that make up the sound.
5. How does sound travel through different mediums?
Sound travels through different mediums at different speeds. It generally travels faster through solids and liquids than through air, and the speed also depends on the temperature and density of the medium.
6. What is sound design?
Sound design is the art and science of creating and manipulating sound for various applications, including film, video games, and live performances.
7. What is noise pollution and what are its effects?
Noise pollution is excessive or unwanted sound that can have negative effects on human health and well-being, causing stress, anxiety, sleep disturbances, and hearing loss.
8. How can I reduce noise pollution in my home?
You can reduce noise pollution in your home by soundproofing the walls, installing thick curtains, sealing gaps around doors and windows, and using noise-canceling devices.
9. What are some emerging trends in audio technology?
Emerging trends in audio technology include spatial audio, virtual reality audio, and artificial intelligence-powered sound design tools.
10. How can I learn more about sound and acoustics?
You can learn more about sound and acoustics by reading books, taking online courses, visiting museums and exhibits dedicated to sound, and joining online communities and forums.