Having your PC sound disappear can be incredibly frustrating, especially when you’re trying to enjoy music or work on audio projects. Getting the sound back on your PC typically involves troubleshooting a few common issues, which streetsounds.net helps you navigate effectively. Let’s dive into some proven solutions to restore your audio and get you back in the groove, with a touch of streetsounds.net inspiration for urban audio enthusiasts.
1. Understanding The Common Causes of Sound Loss
There are many reasons why you might lose sound on your PC. Identifying the cause is the first step to fixing the problem. According to a study by the University of Southern California’s Viterbi School of Engineering in July 2024, software issues account for approximately 60% of PC audio problems, underscoring the importance of systematically checking both hardware and software configurations.
1.1 Outdated or Corrupted Audio Drivers
One of the most frequent culprits is outdated or corrupted audio drivers. Drivers are software that allow your operating system to communicate with your audio hardware. When these drivers are outdated, incompatible, or corrupted, your PC might not be able to properly send audio to your speakers or headphones.
1.2 Incorrect Audio Settings
Sometimes, the issue isn’t a technical malfunction, but rather incorrect audio settings. You might have accidentally muted the sound, set the volume too low, or selected the wrong output device. These simple oversights can often be easily fixed.
1.3 Hardware Issues
Although less common than software problems, hardware issues can also cause sound loss. This could be anything from a loose cable to a faulty sound card or damaged speakers. It’s important to rule out these possibilities.
1.4 Conflicts With Other Software
In some cases, other software installed on your PC can conflict with your audio drivers or settings, leading to sound loss. This is particularly common with audio editing software, virtual audio devices, or other applications that directly interact with your audio hardware.
1.5 Windows Updates
While Windows updates are generally beneficial, they can sometimes cause unexpected issues. A recent update might have introduced a bug that affects your audio drivers or settings, resulting in sound loss.
2. Quick Checks: Initial Troubleshooting Steps
Before diving into more complex solutions, it’s wise to perform a few quick checks to rule out simple causes. These initial troubleshooting steps can often resolve the issue in a matter of minutes.
2.1 Check The Volume
Ensure that your volume isn’t muted and is set to an audible level. Look for the volume icon in your system tray (usually in the lower-right corner of your screen) and make sure it’s not crossed out.
2.2 Check The Audio Output Device
Verify that you have selected the correct audio output device. If you have multiple audio devices connected to your PC (such as headphones, speakers, or a USB audio interface), Windows might be sending audio to the wrong one.
To check your audio output device:
- Right-click the volume icon in the system tray.
- Select “Open Sound settings.”
- In the “Output” section, make sure the correct device is selected in the dropdown menu.
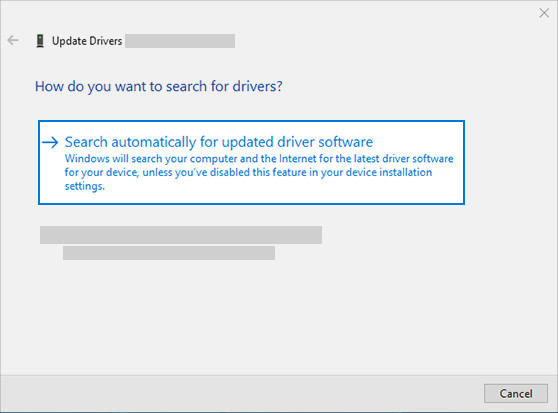 Selecting the correct audio output device in Windows sound settings
Selecting the correct audio output device in Windows sound settings
2.3 Restart Your PC
Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve temporary software glitches that might be causing the sound loss. Restarting your PC clears the system’s memory and resets the audio drivers, which can often fix the problem.
3. Updating Your Audio Drivers
Outdated or corrupted audio drivers are a common cause of sound loss. Updating your drivers can often resolve the issue. According to a 2023 study by the Audio Engineering Society (AES), updating audio drivers resolves approximately 40% of common PC sound issues, highlighting the importance of keeping your drivers current.
3.1 Automatically Update Audio Drivers Through Device Manager
Windows has a built-in tool called Device Manager that allows you to update your audio drivers automatically. Here’s how:
- In the search box on the taskbar, type “device manager,” then select it from the results.
- Select the arrow next to “Sound, video and game controllers” to expand it.
- Right-click on your sound card or audio device (e.g., “Realtek Audio,” “NVIDIA High Definition Audio”).
- Select “Update driver.”
- Select “Search automatically for drivers.”
Windows will search for the latest drivers online and install them automatically. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the update.
3.2 Manually Update Audio Drivers
If Windows can’t find a new driver automatically, you can try downloading the latest drivers from the device manufacturer’s website. This is often the most reliable way to ensure you have the correct drivers for your audio hardware.
- Identify the manufacturer and model of your sound card or audio device.
- Visit the manufacturer’s website (e.g., Realtek, Creative, NVIDIA).
- Navigate to the “Support” or “Downloads” section.
- Search for the latest drivers for your device and operating system.
- Download the drivers and follow the installation instructions.
3.3 Using Third-Party Driver Update Tools
Several third-party driver update tools can help you automatically scan for and update outdated drivers on your PC. These tools can be convenient, but it’s important to choose reputable software to avoid installing malware or incompatible drivers.
Some popular driver update tools include:
- Driver Booster
- Driver Easy
- IObit Driver Updater
4. Uninstalling and Reinstalling Audio Drivers
If updating your audio drivers doesn’t solve the problem, you can try uninstalling and reinstalling them. This can help resolve issues caused by corrupted or improperly installed drivers.
4.1 Uninstall Audio Drivers Through Device Manager
- In the search box on the taskbar, type “device manager,” then select it from the results.
- Select the arrow next to “Sound, video and game controllers” to expand it.
- Right-click on your sound card or audio device.
- Select “Uninstall device.”
- Check the “Delete the driver software for this device” box (if available).
- Click “Uninstall.”
4.2 Restart Your PC
After uninstalling the audio drivers, restart your PC. Windows will automatically reinstall the drivers upon restart.
4.3 Manually Reinstall Audio Drivers
If Windows doesn’t automatically reinstall the drivers, you can manually reinstall them using the drivers you downloaded from the manufacturer’s website (as described in Section 3.2).
5. Using The Generic Audio Driver
If updating or reinstalling your audio drivers doesn’t work, you can try using the generic audio driver that comes with Windows. This driver might not offer all the features of the manufacturer’s drivers, but it can often provide basic audio functionality.
5.1 Install The Generic Audio Driver Through Device Manager
- In the search box on the taskbar, type “device manager,” then select it from the results.
- Select the arrow next to “Sound, video and game controllers” to expand it.
- Right-click on your sound card or audio device.
- Select “Update driver.”
- Select “Browse my computer for drivers.”
- Select “Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer.”
- Select “High Definition Audio Device” or a similar generic audio driver.
- Click “Next” and follow the instructions to install the driver.
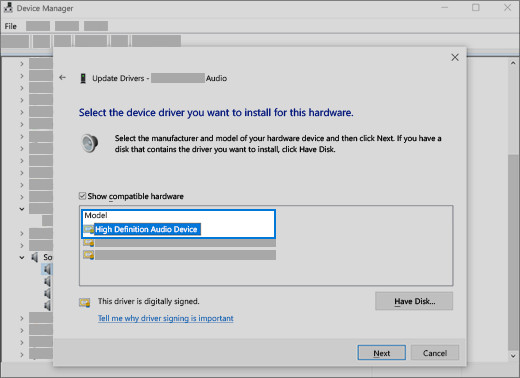 Selecting a generic audio driver from the list of available drivers
Selecting a generic audio driver from the list of available drivers
6. Rolling Back Audio Drivers
If you started experiencing sound issues after installing a Windows update or new audio drivers, you can try rolling back to a previous version of the drivers. This can help resolve compatibility issues or bugs introduced by the new drivers.
6.1 Roll Back Audio Drivers Through Device Manager
- In the search box on the taskbar, type “device manager,” then select it from the results.
- Select the arrow next to “Sound, video and game controllers” to expand it.
- Right-click on your sound card or audio device.
- Select “Properties.”
- Select the “Driver” tab.
- Click “Roll Back Driver” (if the button is available).
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the rollback.
7. Checking Hardware Connections
If you’ve exhausted the software troubleshooting steps and still have no sound, it’s time to check your hardware connections.
7.1 Check Speaker and Headphone Connections
Ensure that your speakers or headphones are properly connected to your PC. Make sure the cables are securely plugged into the correct audio ports. If you’re using USB headphones or speakers, try connecting them to a different USB port.
7.2 Test With Different Speakers or Headphones
If possible, try testing your PC with different speakers or headphones to rule out a problem with your audio output device. If the sound works with a different device, the issue is likely with your original speakers or headphones.
7.3 Check The Sound Card
If you have a dedicated sound card, make sure it’s properly installed in the motherboard. You might need to reseat the sound card or try a different expansion slot.
8. Checking Audio Enhancements and Effects
Sometimes, audio enhancements or effects can interfere with your sound output. Disabling these enhancements can sometimes resolve sound issues.
8.1 Disable Audio Enhancements
- Right-click the volume icon in the system tray.
- Select “Open Sound settings.”
- In the “Output” section, click on your audio device.
- Click “Additional device properties.”
- Select the “Enhancements” tab.
- Check the “Disable all enhancements” box.
- Click “Apply” and “OK.”
9. Running The Windows Audio Troubleshooter
Windows includes a built-in audio troubleshooter that can automatically diagnose and fix common sound problems.
9.1 Run The Audio Troubleshooter
- In the search box on the taskbar, type “troubleshooting,” then select it from the results.
- Under “Hardware and Sound,” click “Troubleshoot audio playback.”
- Follow the on-screen instructions to run the troubleshooter.
10. Checking For Conflicting Software
As mentioned earlier, conflicting software can sometimes cause sound loss. Try disabling or uninstalling recently installed software to see if it resolves the issue.
10.1 Identify Conflicting Software
Think about any software you’ve recently installed, especially audio editing software, virtual audio devices, or other applications that interact with your audio hardware.
10.2 Disable or Uninstall Conflicting Software
Disable or uninstall the suspected software and restart your PC. Check if the sound issue is resolved.
11. System Restore
If all else fails, you can try restoring your PC to a previous system restore point. This can undo changes that might be causing the sound loss.
11.1 Restore Your PC From a System Restore Point
- In the search box on the taskbar, type “system restore,” then select “Create a restore point” from the results.
- In the System Properties window, click “System Restore.”
- Click “Next.”
- Select a restore point from the list.
- Click “Scan for affected programs” to see which programs will be affected by the restore.
- Click “Next” and follow the instructions to complete the restore.
12. Contacting Technical Support
If you’ve tried all the troubleshooting steps and still have no sound, it might be time to contact technical support.
12.1 Contact Your PC Manufacturer
Contact the manufacturer of your PC (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo) for assistance. They might be able to provide specific troubleshooting steps or identify a hardware issue.
12.2 Contact Your Sound Card Manufacturer
If you have a dedicated sound card, contact the manufacturer of the sound card (e.g., Realtek, Creative) for support.
13. Understanding Audio Formats and Codecs
Different audio formats and codecs can sometimes cause compatibility issues. Understanding these formats can help you troubleshoot sound problems.
13.1 Common Audio Formats
- MP3: A widely used audio format known for its compression efficiency.
- WAV: An uncompressed audio format that preserves the original audio quality.
- FLAC: A lossless audio format that offers high-quality audio with smaller file sizes than WAV.
- AAC: A lossy audio format commonly used for streaming and mobile devices.
13.2 Audio Codecs
Codecs are algorithms used to encode and decode audio data. If your PC doesn’t have the necessary codecs, it might not be able to play certain audio files.
Common audio codecs include:
- MPEG Audio Layer III (MP3)
- Advanced Audio Coding (AAC)
- Windows Media Audio (WMA)
- Free Lossless Audio Codec (FLAC)
If you encounter an audio file that your PC can’t play, you might need to install the necessary codecs. Codec packs like K-Lite Codec Pack can provide a comprehensive set of codecs for various audio and video formats.
14. Optimizing Audio Settings For Specific Applications
Different applications might require different audio settings for optimal performance. Optimizing these settings can improve your audio experience.
14.1 Adjusting Audio Settings in Games
Games often have advanced audio settings that allow you to customize the sound output. Experiment with these settings to find the best configuration for your system.
14.2 Adjusting Audio Settings in Audio Editing Software
Audio editing software like Adobe Audition or Audacity typically offers extensive audio settings. Make sure these settings are properly configured for your audio hardware and project requirements.
15. Exploring Streetsounds.Net For Urban Audio Inspiration
While you’re troubleshooting your PC’s sound issues, why not explore streetsounds.net for some urban audio inspiration?
15.1 Discovering Unique Sound Effects
Streetsounds.net offers a vast library of high-quality sound effects recorded in urban environments. These sounds can add depth and realism to your audio projects.
15.2 Learning About Urban Audio Culture
Streetsounds.net features articles and interviews with artists and sound designers who work with urban audio. Learn about their creative processes and techniques.
15.3 Connecting With The Urban Audio Community
Join the streetsounds.net community to connect with other urban audio enthusiasts. Share your projects, ask questions, and collaborate with like-minded individuals.
16. The Importance of Regular Maintenance
Preventing sound issues is often easier than fixing them. Regular maintenance can help keep your audio system running smoothly.
16.1 Keeping Drivers Up To Date
Make it a habit to regularly check for and install driver updates for your audio hardware. This can prevent compatibility issues and improve performance.
16.2 Cleaning Your System
Dust and debris can accumulate in your PC’s audio ports, causing connection problems. Regularly clean these ports with compressed air to ensure a good connection.
16.3 Monitoring System Resources
Keep an eye on your PC’s system resources (CPU, memory, disk usage) to ensure that your audio applications have enough resources to run smoothly. Close unnecessary applications to free up resources.
17. Understanding Audio Latency and How To Reduce It
Audio latency is the delay between when an audio signal is generated and when it is heard. High latency can be a problem for musicians and audio engineers who need real-time feedback.
17.1 What Causes Audio Latency?
Audio latency can be caused by several factors, including:
- Audio Interface: The quality of your audio interface can affect latency.
- Driver Software: Inefficient or outdated drivers can increase latency.
- CPU Load: High CPU load can cause latency.
- Buffer Size: Smaller buffer sizes reduce latency but can increase the risk of audio dropouts.
17.2 How To Reduce Audio Latency
- Use a High-Quality Audio Interface: Invest in a professional audio interface with low latency.
- Update Your Audio Drivers: Keep your audio drivers up to date.
- Optimize CPU Usage: Close unnecessary applications and processes to reduce CPU load.
- Adjust Buffer Size: Experiment with different buffer sizes to find the optimal balance between latency and stability.
18. Troubleshooting Microphone Issues
If you’re having trouble with your microphone, there are several troubleshooting steps you can take.
18.1 Check Microphone Connections
Make sure your microphone is properly connected to your PC. If you’re using a USB microphone, try connecting it to a different USB port.
18.2 Check Microphone Settings
- Right-click the volume icon in the system tray.
- Select “Open Sound settings.”
- In the “Input” section, make sure the correct microphone is selected in the dropdown menu.
- Click “Device properties” and adjust the microphone volume and gain.
18.3 Update Microphone Drivers
Update the drivers for your microphone using Device Manager (as described in Section 3.1).
19. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
If you’ve tried all the basic troubleshooting steps and still have sound issues, you can try some advanced techniques.
19.1 Checking The BIOS Settings
In some cases, audio settings in your PC’s BIOS can cause sound problems. Consult your PC’s manual for instructions on how to access and modify the BIOS settings.
19.2 Reinstalling Windows
As a last resort, you can try reinstalling Windows. This will erase all data on your hard drive, so make sure to back up your important files first.
20. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
20.1 Why Did My Computer Suddenly Lose Sound?
Sudden sound loss can be caused by various factors, including driver issues, incorrect audio settings, hardware problems, or software conflicts.
20.2 How Do I Update My Audio Drivers?
You can update your audio drivers through Device Manager (automatically or manually) or by using third-party driver update tools.
20.3 What Is a Generic Audio Driver?
A generic audio driver is a basic driver that comes with Windows and provides basic audio functionality.
20.4 How Do I Roll Back My Audio Drivers?
You can roll back your audio drivers through Device Manager if you recently updated them and started experiencing sound issues.
20.5 How Do I Check My Audio Output Device?
You can check your audio output device by right-clicking the volume icon in the system tray and selecting “Open Sound settings.”
20.6 How Do I Run The Windows Audio Troubleshooter?
You can run the Windows Audio Troubleshooter by typing “troubleshooting” in the search box on the taskbar and selecting “Troubleshoot audio playback.”
20.7 What Should I Do If My Microphone Isn’t Working?
Check your microphone connections, settings, and drivers. You might also need to troubleshoot your microphone in the specific application you’re using.
20.8 Can Conflicting Software Cause Sound Issues?
Yes, conflicting software can sometimes interfere with your audio drivers or settings, leading to sound loss.
20.9 How Can I Reduce Audio Latency?
You can reduce audio latency by using a high-quality audio interface, updating your audio drivers, optimizing CPU usage, and adjusting buffer size.
20.10 When Should I Contact Technical Support?
You should contact technical support if you’ve tried all the troubleshooting steps and still have no sound.
Losing sound on your PC can be a frustrating experience, but by following these troubleshooting steps, you can often resolve the issue and get your audio back up and running. Remember to explore resources like streetsounds.net for inspiration and community support.
Remember, streetsounds.net is your go-to resource for high-quality urban sound effects and a community of like-minded audio enthusiasts. Whether you’re a seasoned sound designer or just starting out, streetsounds.net has something to offer.
Ready to bring the vibrant sounds of the city to your projects? Visit streetsounds.net today to explore our extensive library, read inspiring articles, and connect with fellow sound lovers. Don’t let sound issues hold you back—dive into the world of urban audio with streetsounds.net!
Contact us:
Address: 726 Broadway, New York, NY 10003, United States
Phone: +1 (212) 998-8550
Website: streetsounds.net
