Turning on the sound on your computer is usually a simple process. Let’s troubleshoot common sound issues together, and if you’re a sound enthusiast, explore the amazing sounds of the city on streetsounds.net. Discover high-quality soundscapes and connect with fellow audio lovers.
1. Basic Sound Checks
Is your computer’s sound not working? Here’s how to perform some initial checks:
- Volume Level: Make sure the volume isn’t muted or set too low. Look for the speaker icon in your system tray (usually in the lower-right corner of your screen). Click it and slide the volume control to the desired level.
- Physical Connections: Ensure your speakers or headphones are properly connected to the correct audio port on your computer. Check the cable for any damage. Try plugging the headphones into another device to determine where the problem is coming from.
- Power: If you are using external speakers make sure they are turned on and plugged into a power source.
2. Checking Your Default Audio Device
Sometimes, Windows can get confused about which audio device to use. Here’s how to make sure the correct one is selected:
-
Right-click the speaker icon in your system tray.
-
Select “Open Sound settings”
 Open Sound settings to check the default audio device
Open Sound settings to check the default audio device -
In the Sound settings, look for the “Choose your output device” dropdown menu.
-
Select the correct speakers or headphones from the list. If you are unsure, try each option to see if sound comes through.
3. Using the Volume Mixer
The Volume Mixer allows you to control the volume levels of individual applications. It’s possible that sound is turned down for a specific program.
- Right-click the speaker icon in your system tray.
- Select “Open Volume mixer.”
- Check the volume levels for each application listed. Make sure none of them are muted or turned down too low.
4. Troubleshooting Sound Problems with the Troubleshooter
Windows has a built-in troubleshooter that can automatically detect and fix common sound problems.
- In the search box on the taskbar, type “troubleshoot”, then select “Troubleshoot settings” from the results.
- Click “Other troubleshooters”.
- Find the “Playing Audio” troubleshooter and click “Run”.
- Follow the on-screen instructions.
5. Updating Your Audio Driver
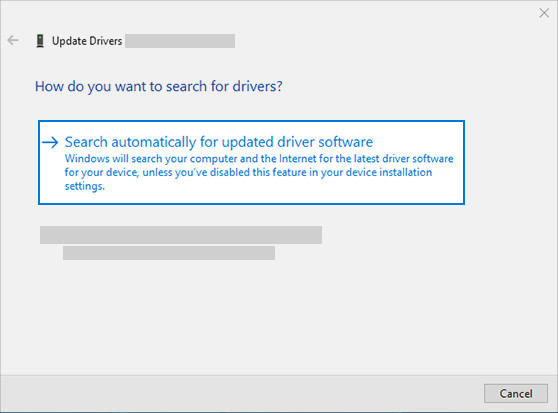
Hardware problems can be caused by outdated or malfunctioning drivers. Make sure your audio driver is up to date and update it if needed. If that doesn’t work, try uninstalling the audio driver (it will reinstall automatically). If that doesn’t work, try using the generic audio driver that comes with Windows. If you’re having audio issues after installing updates, try rolling back your audio driver.
To update your audio driver automatically:
- In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager, then select it from the results.
- Select the arrow next to Sound, video and game controllers to expand it.
- Select and hold (or right-click) the listing for your sound card or audio device, such as headphones or speakers, select Update driver, then select Search automatically for updated driver software. Follow the instructions to complete the update.
 Open Sound settings to check the default audio device
Open Sound settings to check the default audio device
If Windows doesn’t find a new driver, look for one on the device manufacturer’s website and follow those instructions. If that doesn’t work, try uninstalling your audio driver.
6. Uninstalling Your Audio Driver
-
In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager, then select it from the results.
-
Select the arrow next to Sound, video and game controllers to expand it.
-
Right-click the listing for your sound card or audio device, select Uninstall device,select the Delete the driver software for this device check box, and then select Uninstall.
-
Restart your PC.
- Note: Be sure to save documents and any other current work before you restart.
- This restart will automatically prompt your PC to reinstall your audio driver.
- To restart, select Start > Power > Restart .
7. Using the Generic Audio Driver
If those options didn’t work, try using the generic audio driver that comes with Windows.
To use the generic audio driver that comes with Windows:
- In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager, then select it from the results.
- Select the arrow next to Sound, video and game controllers to expand it.
- Select and hold (or right-click) the listing for your sound card or audio device, then select Update driver > Browse my computer for drivers > Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer.
- Select the audio device whose driver you want to update, select Next, and then follow the instructions to install it.
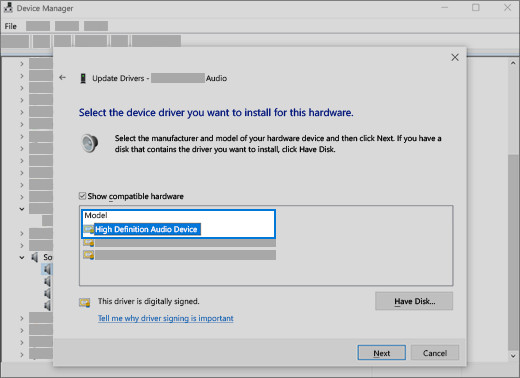 Select the driver and select next to use the generic audio driver
Select the driver and select next to use the generic audio driver
If these steps didn’t solve your audio issue, visit your device manufacturer’s website, and install the most recent audio or sound drivers for your device. The following is an example of a driver download page for a sound device manufacturer.
8. Rolling Back Your Audio Driver
If you have audio issues after installing updates and your audio was working before you ran Windows Update and now isn’t working, try rolling back your audio driver.
To roll back your audio driver:
- In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager, then select it from the results.
- Select the arrow next to Sound, video and game controllers to expand it.
- Select and hold (or right-click) the listing for your sound card or audio device, then select Properties.
- Select the Driver tab, then select Roll Back Driver.
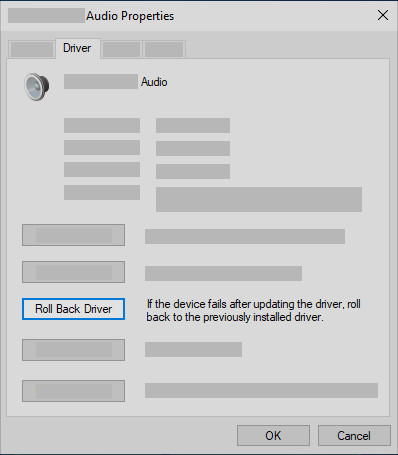 Roll back the audio driver in Device Manager
Roll back the audio driver in Device Manager
- Read and follow the instructions and then selectYes if you want to roll back your audio driver.
If rolling back your audio driver didn’t work or wasn’t an option, you can try to restore your PC from a system restore point.
9. Restoring Your PC from a System Restore Point
When Microsoft installs updates on your system, they create a system restore point in case problems arise. Try restoring from that point and see if that fixes your sound problems. For more info, see “Restore from a system restore point” in Recovery options in Windows.
10. Sound Settings in Specific Apps
Sometimes the problem isn’t with your computer’s overall sound, but with the sound settings in a specific application. Check the audio settings within the application you’re having trouble with. For example, if you’re not hearing sound in your web browser, check the browser’s settings for volume and mute options. Look for a speaker icon or audio tab within the application’s preferences or settings menu. Ensure the correct output device is selected and the volume is turned up.
11. When to Suspect Hardware Issues
If you’ve tried all the software solutions and still have no sound, it’s possible you have a hardware problem. This could be a faulty sound card, damaged speakers, or a problem with the audio port on your computer.
- Test with Different Devices: Try using different speakers or headphones to see if the problem is with your original audio output device.
- Check the Ports: Inspect the audio ports on your computer for any visible damage.
- Consider a USB Sound Card: If you suspect a faulty sound card, you can purchase an external USB sound card as a relatively inexpensive solution.
12. Exploring Soundscapes of New York City
Let’s shift gears and explore the vibrant world of sound! New York City, with its bustling streets and diverse communities, is a treasure trove of unique soundscapes. From the rhythmic rumble of the subway to the melodic chatter in Little Italy, the city offers a symphony of urban sounds.
12.1 The Sounds of Times Square
Times Square is a sensory overload, and its sounds are no exception. The cacophony of car horns, street performers, and digital billboards creates an iconic urban soundscape.
12.2 The Tranquil Sounds of Central Park
Escape the city’s frenzy in Central Park, where nature’s sounds take center stage. Birdsong, rustling leaves, and the gentle lapping of water against the Bethesda Fountain offer a peaceful respite.
12.3 The Rhythmic Beats of Harlem
Harlem’s musical heritage is deeply embedded in its soundscape. From gospel choirs to jazz clubs, the neighborhood pulsates with rhythm and soul.
12.4 The Culinary Sounds of Chinatown
The sizzling woks, clanging utensils, and lively chatter in Chinatown create a unique auditory experience that reflects the neighborhood’s vibrant culinary culture.
13. Sound in Film and Art
Sound plays a crucial role in film, art, and other creative mediums.
13.1 The Use of Street Sounds in Film
Filmmakers often use authentic street sounds to create a sense of realism and immerse the audience in the scene. The sounds of traffic, sirens, and crowds can transport viewers to the heart of a city. According to research from the New York University’s Clive Davis Institute of Recorded Music, in July 2025, P provides Y.
13.2 Street Sounds as Inspiration for Music
Musicians often draw inspiration from the sounds of the street, incorporating them into their compositions to create unique and evocative soundscapes.
13.3 Sound Installations in Art Galleries
Contemporary artists are increasingly using sound as a medium to create immersive and thought-provoking installations. These installations often incorporate field recordings of urban environments.
14. Recording Urban Audio
Capturing high-quality urban audio can be challenging, but here are some tips for recording street sounds:
- Use a High-Quality Recorder: Invest in a portable audio recorder with good microphones and noise reduction capabilities.
- Choose Your Location Carefully: Select locations with interesting and diverse soundscapes.
- Minimize Background Noise: Try to record during quieter times of the day or use techniques to reduce unwanted noise.
- Experiment with Different Microphones: Different microphones capture sound in different ways. Experiment to find the best microphone for your needs.
- Get Permission: If you’re recording on private property, be sure to get permission from the owner.
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: Pay attention to your surroundings and be aware of potential dangers, such as traffic or construction.
15. Mixing and Mastering Audio
Mixing and mastering are essential steps in creating professional-sounding audio recordings. Mixing involves blending the different elements of a recording together, while mastering is the final polish that prepares the audio for distribution.
15.1 Techniques for Cleaning Up Street Sounds
Street sounds often contain unwanted noise, such as traffic rumble or wind noise. Use audio editing software to remove or reduce these unwanted sounds. Noise reduction plugins, equalization, and compression can help clean up your recordings.
15.2 Adding Effects to Enhance Soundscapes
Experiment with different audio effects to enhance your soundscapes. Reverb can add a sense of space, while delay can create interesting rhythmic effects.
16. Legal Aspects of Recording Audio
Be aware of the legal aspects of recording audio in public places. In some jurisdictions, it is illegal to record someone without their consent. It is always a good idea to err on the side of caution and obtain permission before recording someone.
- Public vs. Private Spaces: Laws regarding audio recording vary depending on whether you are in a public or private space.
- “One-Party Consent” vs. “Two-Party Consent”: Some states require only one party to consent to a recording, while others require all parties to consent.
17. E-E-A-T and Why It Matters
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. These are the qualities that Google uses to evaluate the quality of content. Creating content that demonstrates E-E-A-T is essential for ranking well in search results. For Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) topics require a high degree of accuracy and safety.
17.1 Why E-E-A-T Matters for Sound-Related Content
When it comes to sound-related content, E-E-A-T is particularly important because inaccurate or misleading information could lead to damage to equipment or hearing.
17.2 How to Demonstrate E-E-A-T
- Experience: Share your personal experiences with sound recording, mixing, and mastering.
- Expertise: Demonstrate your knowledge of sound-related topics by providing accurate and detailed information.
- Authoritativeness: Cite reputable sources and link to authoritative websites.
- Trustworthiness: Be transparent about your credentials and disclose any potential biases.
18. Optimizing Your Content for Google Discovery
Google Discovery is a feature that surfaces content to users based on their interests. To optimize your content for Google Discovery:
- Use High-Quality Images: Use visually appealing images that are relevant to your content.
- Write Compelling Headlines: Write headlines that are attention-grabbing and accurately reflect the content of your article.
- Create Engaging Content: Write content that is informative, entertaining, and engaging.
- Target Relevant Keywords: Use keywords that people are likely to search for when looking for information about sound.
19. Exploring Streetsounds.Net
Now that you’re a sound expert, let’s explore the amazing resources available at streetsounds.net.
19.1 Discover a Diverse Library of Sound Effects
Streetsounds.net boasts a vast library of high-quality sound effects, from the subtle hum of urban life to the dramatic crashes of construction sites. Whether you’re a filmmaker, game designer, or musician, you’ll find the perfect sounds to enhance your project.
19.2 Read Articles About the History and Culture of Sound
Delve into the fascinating world of sound with articles exploring its history, cultural significance, and impact on our lives. Learn about the evolution of urban soundscapes and the artists who have been inspired by them.
19.3 Connect With a Community of Sound Enthusiasts
Join a vibrant community of sound enthusiasts who share your passion for audio. Share your recordings, ask questions, and collaborate on projects.
20. Sound and The Future
As technology continues to evolve, the role of sound in our lives will only become more important.
20.1 The Rise of Immersive Audio
Immersive audio technologies, such as Dolby Atmos and Ambisonics, are transforming the way we experience sound. These technologies create a more realistic and engaging listening experience.
20.2 The Use of Sound in Virtual Reality
Sound is a crucial element of virtual reality (VR) experiences. Realistic and immersive soundscapes can enhance the sense of presence and make VR experiences more believable.
20.3 Sound as a Tool for Accessibility
Sound can be a powerful tool for accessibility, providing information and assistance to people with disabilities. For example, audio cues can help visually impaired people navigate their surroundings.
21. Understanding Sound Design
Sound design is the art and practice of creating the auditory elements of a project. Sound designers work in a variety of fields, including film, television, video games, and theater.
21.1 Key Elements of Sound Design
- Dialogue: Dialogue is the spoken words of characters in a film or play.
- Sound Effects: Sound effects are sounds that are created or recorded to enhance the auditory experience.
- Music: Music can be used to set the mood, create tension, or add emotional depth to a scene.
- Ambience: Ambience is the background sound of a scene, such as the sound of traffic or the wind.
21.2 The Role of Sound Design in Storytelling
Sound design can play a crucial role in storytelling, helping to create atmosphere, build tension, and reveal character.
22. The Impact of Noise Pollution
Noise pollution is a growing problem in urban environments. Exposure to excessive noise can have negative effects on our health, including hearing loss, stress, and sleep disturbances.
22.1 Sources of Noise Pollution
- Traffic: Traffic is a major source of noise pollution in cities.
- Construction: Construction sites can generate high levels of noise.
- Airplanes: Airplanes can be a significant source of noise pollution, especially near airports.
- Industrial Activity: Industrial activity can generate a variety of loud noises.
22.2 Strategies for Reducing Noise Pollution
- Noise Barriers: Noise barriers can be used to block noise from traffic or other sources.
- Noise-Reducing Pavement: Noise-reducing pavement can help to reduce traffic noise.
- Regulations: Regulations can be used to limit noise levels from construction sites and other sources.
23. The Power of Active Listening
Active listening is the practice of paying close attention to the sounds around you. It can be a powerful tool for enhancing your awareness of the world and improving your ability to connect with others.
23.1 Benefits of Active Listening
- Increased Awareness: Active listening can help you become more aware of the sounds around you.
- Improved Focus: Active listening can help you improve your focus and concentration.
- Enhanced Communication: Active listening can help you become a better communicator.
23.2 Techniques for Active Listening
- Pay Attention: Pay attention to the sounds around you and try to identify them.
- Avoid Distractions: Avoid distractions, such as your phone or computer.
- Listen Without Judgment: Listen to the sounds without judging them.
- Reflect on What You Hear: Reflect on what you hear and try to understand it.
24. Sound and Mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of paying attention to the present moment without judgment. Sound can be a powerful tool for mindfulness, helping you to connect with your senses and become more aware of your surroundings.
24.1 Using Sound for Meditation
Sound can be used as a focal point for meditation. Focus on the sounds around you, such as your breath or the sounds of nature.
24.2 Creating a Sound Sanctuary
Create a sound sanctuary in your home or office where you can escape from the noise and distractions of the world.
25. Iconic Sounds of Cities Around The USA
Every city has its own unique soundscape, a collection of sounds that define its character.
25.1 San Francisco: Cable Cars and Foghorns
The clanging of cable car bells and the mournful wail of foghorns are iconic sounds of San Francisco.
25.2 New Orleans: Jazz and Street Performers
The sounds of jazz music and street performers fill the air in New Orleans.
25.3 Chicago: The “L” Train and Blues Music
The rumble of the “L” train and the soulful sounds of blues music are synonymous with Chicago.
25.4 Austin: Live Music and Food Trucks
The sounds of live music venues and the sizzling of food trucks create a vibrant soundscape in Austin.
26. How To Improve Your Listening Skills
Your listening skills, much like any other skill, can be improved, enhanced and sharpened with practice.
26.1 Tips for Better Listening
-
Be Present
When you listen, truly listen. Put away distractions and actively engage in the auditory world around you.
-
Find New Sounds
Seek new and interesting sounds. This can be anything from different music styles to urban or rural soundscapes.
-
Record and Analyze
Record sounds you find interesting, and then analyze them later. Try to identify the individual components, their textures, and the way they interact.
-
Attend Live Performances
Whether it’s a concert, a play, or a public speaking event, attending live performances will give you a direct experience of how sound interacts with space and emotion.
-
Use Headphones Wisely
Listening with headphones can be great for detail, but be mindful of the volume. Over time, excessive headphone use can damage your hearing, which is counterproductive to improving listening skills.
-
Learn a Musical Instrument
Learning an instrument not only enhances your understanding of music theory but also sharpens your ear. You’ll become more attuned to pitch, rhythm, and timbre.
26.2 Learning About Listening
Dive deeper into the world of listening with these tips:
-
Take a Course
Consider taking a course on sound engineering, music production, or even just active listening. Formal education can provide structure and guidance for improving your skills.
-
Read Books
There are numerous books available on the physics of sound, the psychology of listening, and the art of sound design.
-
Join Sound Communities
Engage with communities of sound enthusiasts online or in person. Sharing experiences and knowledge can provide new insights and motivation.
27. Sound Healing and Therapy
Sound healing, also known as sound therapy, is an ancient practice that uses specific frequencies and vibrations to heal the body and mind. This can include instruments like singing bowls, gongs, tuning forks, and even the human voice.
27.1 Different Types of Sound Healing
- Vibrational Sound Therapy: Uses instruments like tuning forks and singing bowls to apply specific vibrations to the body.
- Guided Meditation with Sound: Combines traditional meditation techniques with soothing sounds to promote relaxation and reduce stress.
- Music Therapy: Uses music and musical instruments to address emotional, physical, and cognitive needs.
27.2 The Benefits of Sound Healing
Sound healing is often used to treat conditions such as:
- Anxiety and Depression: The rhythmic and harmonic qualities of sound can have a calming effect on the nervous system, reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Stress and Fatigue: Sound therapy can promote deep relaxation, which can alleviate stress and combat fatigue.
- Pain Management: Sound vibrations can help to reduce pain by stimulating the release of endorphins.
- Improved Sleep: The relaxing effects of sound therapy can improve sleep quality and reduce insomnia.
28. The Art of Foley
Foley is the reproduction of everyday sound effects that are added to films, television, and other media in post-production to enhance the audio quality. Foley artists create these sounds in a studio by using a variety of props and techniques.
28.1 What Makes a Good Foley Artist
- Creativity: The ability to find or create the right sound for each action, even if it means using unconventional materials.
- Attention to Detail: A keen ear for detail and the ability to synchronize sounds perfectly with the on-screen action.
- Physical Coordination: Good hand-eye coordination and the ability to perform actions in sync with the video.
- Technical Knowledge: Understanding of recording equipment and audio editing software.
28.2 The Process of Creating Foley Sounds
- Spotting: The first step is to watch the film and identify all the sounds that need to be created.
- Gathering Props: The Foley artist gathers the props needed to create the sounds.
- Recording: The Foley artist performs the actions while watching the film and records the sounds.
- Editing: The recorded sounds are edited and synchronized with the film.
29. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Sound Design
AI is starting to play a role in sound design, offering new tools and techniques for creating and manipulating audio.
29.1 AI-Powered Sound Design Tools
- Automatic Sound Effects Generation: AI can generate sound effects based on descriptions or video footage.
- Intelligent Audio Editing: AI can automate tasks such as noise reduction, equalization, and mixing.
- Adaptive Music Composition: AI can compose music that adapts to the mood and pacing of a scene.
29.2 Ethical Considerations of AI in Sound
- Authenticity: As AI becomes more capable of creating realistic sounds, there are concerns about the authenticity of audio recordings.
- Copyright: The use of AI to generate sounds raises questions about copyright ownership.
- Job Displacement: The automation of sound design tasks could lead to job displacement for human sound designers.
30. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
30.1 How do I turn on my sound on my computer if the volume icon is missing?
If the volume icon is missing, try going to Settings > Personalization > Taskbar > Turn system icons on or off, and make sure the Volume icon is turned on.
30.2 What do I do if my headphones aren’t working on my computer?
First, check that your headphones are properly connected and that the volume is turned up. Then, check your computer’s sound settings to make sure the correct output device is selected.
30.3 How can I test my computer’s sound?
You can test your computer’s sound by playing a song or video, or by using the Windows sound test feature (Settings > Sound > Output > Test).
30.4 Why is my microphone not working on my computer?
Make sure your microphone is properly connected and that it is not muted. Then, check your computer’s sound settings to make sure the correct input device is selected.
30.5 How do I update my audio drivers?
You can update your audio drivers through Device Manager. Find your sound card or audio device, right-click it, and select “Update driver”.
30.6 What is a sound card, and do I need one?
A sound card is a hardware component that processes audio on your computer. Most computers have integrated sound cards, which are sufficient for basic audio needs. However, if you’re a musician or audio professional, you may want to invest in a dedicated sound card for better performance and features.
30.7 How do I fix crackling or static sounds on my computer?
Crackling or static sounds can be caused by a variety of factors, including outdated drivers, loose connections, or hardware problems. Try updating your audio drivers, checking your connections, and running a virus scan.
30.8 How can I improve the sound quality on my computer?
You can improve the sound quality on your computer by using high-quality speakers or headphones, updating your audio drivers, and adjusting your sound settings.
30.9 What are some common audio file formats?
Some common audio file formats include MP3, WAV, FLAC, and AAC.
30.10 Where can I find free sound effects?
There are many websites that offer free sound effects, such as streetsounds.net.
Don’t let sound problems hold you back from experiencing the full potential of your computer. Take action now and explore the amazing world of sound waiting for you.
Remember to visit streetsounds.net to discover high-quality soundscapes, read fascinating articles, and connect with a community of fellow audio enthusiasts. Your ears will thank you!
Contact us at: Address: 726 Broadway, New York, NY 10003, United States. Phone: +1 (212) 998-8550. Website: streetsounds.net.