The violin makes sound through a fascinating interplay of vibrations and amplification, a process we at streetsounds.net are excited to explore. By understanding this intricate mechanism and the factors that influence it, you can unlock the full potential of your instrument and elevate your musical journey. Dive in to discover the mechanics of sound production, the impact of materials, and how streetsounds.net helps you find the perfect sonic landscape.
1. What Components of the Violin Contribute to Sound Production?
The violin’s sound production relies on several key components working in harmony: strings, bridge, soundpost, bass bar, body, and f-holes. These elements create and amplify vibrations to produce the instrument’s characteristic tones.
The violin is a complex instrument where each part plays a crucial role in creating its beautiful sound. Let’s break down each component:
- Strings: The source of the initial vibration. When bowed or plucked, they vibrate at a specific frequency, determining the pitch of the note.
- Bridge: A carefully shaped piece of wood that transfers the strings’ vibrations to the body of the violin. Its shape and density significantly affect the tone.
- Soundpost: A small dowel of wood placed inside the violin, connecting the top and back plates. It transmits vibrations and influences the instrument’s resonance.
- Bass Bar: A strip of wood glued to the underside of the top plate, running lengthwise. It helps distribute vibrations across the top plate, enhancing the lower frequencies.
- Body: The hollow resonating chamber of the violin. Its shape, size, and the wood used in its construction are critical to the instrument’s overall sound.
- F-holes: The stylized openings on the violin’s top plate. They allow the sound to project from the body and influence the instrument’s resonance.
By understanding how each component contributes to the overall sound, musicians can better appreciate the craftsmanship involved in creating a violin and make informed decisions about instrument selection and maintenance. According to a study by the Catgut Acoustical Society, the interaction between these components is vital for producing a balanced and resonant sound.
2. How Do Vibrations Lead to Sound in a Violin?
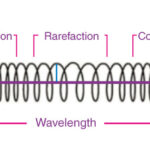
Vibrations initiate sound production in a violin. These vibrations, created by bowing or plucking the strings, are transferred and amplified through various components, ultimately resulting in the violin’s distinct sound.
Vibration is the core of how a violin generates sound. The process begins when the musician draws a bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. These vibrations travel through the bridge, which acts as a crucial intermediary, transmitting the energy to the body of the violin. Inside the violin, the soundpost and bass bar play essential roles in distributing these vibrations throughout the instrument. The soundpost, a small dowel connecting the top and back plates, efficiently transfers vibrations, while the bass bar, running along the underside of the top plate, enhances the instrument’s resonance.
The violin’s body, carefully shaped with specific arching and contours, is designed to vibrate in response to these incoming vibrations. This sympathetic vibration amplifies the sound, projecting it outwards through the f-holes, the characteristic openings on the violin’s top. The size and shape of the f-holes are not merely aesthetic; they play a vital role in shaping the tonal qualities of the violin.
The interaction between these components creates a complex system of resonance, where the vibrations are amplified and shaped to produce the rich, expressive sound that the violin is known for. Understanding this process allows musicians to appreciate the intricacies of their instrument and make informed decisions about technique, setup, and maintenance to achieve the desired tonal qualities.
3. How Does the Violin’s Shape Affect Its Sound Quality?
The violin’s shape significantly influences its sound quality. The arching of the top and bottom plates, along with the size and shape of the f-holes, affects the instrument’s resonance and tonal characteristics.
The shape of a violin is not just for aesthetics; it’s fundamental to its sound production. The curves and contours of the top and bottom plates, known as arching, play a crucial role in determining how the instrument vibrates. A well-designed arching allows the plates to move freely, enhancing the violin’s resonance. The specific shape of the arching can affect tonal qualities, with some designs favoring certain frequencies over others.
The f-holes, those elegant openings on the violin’s top, also have a significant impact on sound. The area of the front plate between the f-holes is particularly responsive to vibration, so the length and shape of the f-holes can influence the instrument’s overall sound profile. Violins with longer f-holes tend to have a different sound than those with shorter f-holes.
Skilled luthiers carefully craft violins, paying close attention to the shape of the plates and f-holes to achieve specific sound characteristics. They may experiment with different arching patterns, f-hole sizes, and wood types to create instruments with unique tonal qualities. This meticulous approach allows them to tailor the violin’s sound to suit the preferences of different musicians and musical styles.
4. What Role Do Different Violin Strings Play in Sound?
Different violin strings significantly impact the instrument’s sound. Factors like material, thickness, tension, and condition of the strings all contribute to the overall tone and responsiveness of the violin.
Violin strings are more than just accessories; they are fundamental to the instrument’s sound. Their material, thickness, tension, and condition all play crucial roles in shaping the violin’s tonal characteristics.
- Material: The material from which a string is made has a significant impact on its sound. Gut core strings, for example, are known for producing warm, rich tones, while metal core strings tend to create brighter, more focused sounds.
- Thickness: The thickness of a string also affects its sound. Thicker strings generally produce a fuller, bigger sound, but they may be less responsive than thinner strings. Thinner strings, on the other hand, are more responsive and tend to create a brighter, clearer sound.
- Tension: The tension of a string, which refers to how tight or loose it is when tuned to pitch, also influences its sound. Tightening the string increases its pitch, while loosening it lowers the pitch. The tension also affects the string’s responsiveness and overall tone.
- Condition: The condition of a string is essential for maintaining its sound quality. Old, worn strings can lose their vibrancy and produce a dull or scratchy sound. Regularly replacing violin strings is necessary to keep the instrument sounding its best.
Experimenting with different types of strings can significantly impact a violin’s sound, allowing musicians to tailor their instrument’s tone to suit their individual preferences and playing styles.
5. How Does the Violin Bow Influence the Sound?
The violin bow significantly influences the sound produced. Its quality, weight, balance, action, and stiffness all affect the tones a violin can create, making bow selection a crucial part of achieving the desired sound.
The violin bow is not merely a tool for creating vibration; it’s an integral part of the instrument that significantly influences the sound. A higher-quality bow is likely to produce a better sound than a lower-quality one, but beyond quality, the bow’s impact on sound comes down to personal preference.
- Weight: A heavier bow can produce a fuller, more powerful sound, while a lighter bow may offer greater agility and responsiveness.
- Balance: A well-balanced bow feels comfortable in the hand and allows for effortless control over the sound.
- Action: The action of a bow refers to how easily it responds to the player’s movements. A bow with good action allows for precise control over dynamics and articulation.
- Stiffness: The stiffness of a bow affects its responsiveness and tonal qualities. A stiffer bow may produce a brighter, more focused sound, while a more flexible bow may offer a warmer, more mellow tone.
Ultimately, the best way to find the right bow is to experiment with different models and find one that complements the player’s technique and musical style.
6. How Does Rosin Affect the Sound a Violin Produces?
Rosin is essential for creating sound on a violin. It provides the necessary friction between the bow hair and strings, enabling vibration. The amount, quality, and type of rosin used can all affect the violin’s sound.
Rosin is a crucial element in violin playing, enabling the bow to grip the strings and produce sound. Without rosin, the bow hair would simply slide across the strings without creating any vibration. The amount of rosin applied, as well as its quality and type, can significantly affect the sound.
- Amount: Applying the right amount of rosin is essential. Too much rosin can result in a harsh, scratchy tone, while too little rosin can cause the bow to slip and produce a weak, inconsistent sound.
- Quality: The quality of rosin also matters. High-quality rosin is made from pure ingredients and produces a smooth, consistent grip on the strings. Low-quality rosin may contain impurities that can negatively affect the sound.
- Type: Different types of rosin are available, each with unique properties that can affect the sound. Some rosins are formulated for specific climates or playing styles, while others are designed to enhance certain tonal qualities.
Experimenting with different rosins can help violinists fine-tune their instrument’s sound and find the perfect match for their playing style.
7. What Happens When a Violin Isn’t Producing Sound?
If a violin isn’t producing sound, the issue could stem from several factors. These include problems with the instrument’s setup, such as a poorly fitted bridge or loose strings, or issues with the bow, like insufficient rosin.
When a violin fails to produce sound, it can be frustrating for the musician. However, identifying the cause can often lead to a simple solution. Here are some common reasons why a violin might not be producing sound:
- Instrument Setup:
- Bridge: Ensure the bridge is properly fitted and positioned correctly on the violin. A bridge that is too high, too low, or improperly shaped can impede the transfer of vibrations.
- Strings: Check that the strings are properly tightened and tuned to the correct pitch. Loose strings will not vibrate effectively and produce little to no sound.
- Bow Issues:
- Rosin: As mentioned earlier, rosin is essential for creating friction between the bow hair and strings. If the bow has not been rosined recently, or if the rosin has worn off, the bow may slip across the strings without producing sound.
- Bow Hair: Inspect the bow hair for damage or excessive wear. Broken or worn hairs can reduce the bow’s ability to grip the strings.
- Other Factors:
- Soundpost: In rare cases, the soundpost inside the violin may have fallen over or shifted out of position. This can significantly reduce the instrument’s resonance and sound output.
- Cracks or Damage: Inspect the violin for any cracks or damage to the body. Cracks can disrupt the instrument’s vibration and reduce its sound quality.
If you’ve checked all of these factors and your violin is still not producing sound, it may be time to consult a professional luthier or music store for further assistance.
8. How Can a Violinist Optimize Their Instrument for Better Sound?
A violinist can optimize their instrument for better sound by selecting high-quality components, ensuring proper setup and maintenance, and experimenting with different strings and bows to find the best match for their playing style.
Optimizing a violin for better sound involves a combination of careful component selection, proper setup and maintenance, and experimentation to find the right match for the player’s individual style. Here are some key steps that violinists can take to enhance their instrument’s sound:
- Select High-Quality Components:
- Strings: Experiment with different string materials, thicknesses, and tensions to find the strings that produce the desired tonal qualities.
- Bow: Invest in a high-quality bow that complements the player’s technique and musical style. Consider factors such as weight, balance, action, and stiffness.
- Rosin: Choose a rosin that provides a smooth, consistent grip on the strings without producing excessive harshness.
- Ensure Proper Setup and Maintenance:
- Bridge: Have the bridge properly fitted and positioned by a qualified luthier.
- Soundpost: Ensure the soundpost is correctly positioned and in good condition.
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the violin regularly to remove dust and rosin buildup, which can dampen the sound.
- Experimentation:
- String Combinations: Try different combinations of strings to find the optimal balance of tone and responsiveness.
- Bow Techniques: Experiment with different bowing techniques to explore the instrument’s full range of tonal possibilities.
- Listening and Feedback: Record your playing and listen critically to identify areas for improvement. Seek feedback from experienced musicians or teachers.
By taking these steps, violinists can unlock their instrument’s full potential and achieve a richer, more expressive sound.
9. What Is the Significance of Violin Maintenance in Sound Quality?
Regular maintenance is crucial for preserving and optimizing a violin’s sound quality. Cleaning, proper storage, and timely repairs can prevent damage and ensure the instrument continues to produce the best possible sound.
Consistent upkeep is essential for preserving the exceptional sound of a violin. Just as a finely tuned car requires routine maintenance, a violin benefits from regular care to ensure it continues to produce its best possible sound. Over time, dust, rosin buildup, and environmental factors can negatively impact the instrument’s tone and playability. Here are some key aspects of violin maintenance and their significance in sound quality:
- Cleaning: Regularly cleaning the violin with a soft, lint-free cloth removes dust and rosin buildup from the body, strings, and bow. This prevents the accumulation of debris that can dampen the sound and affect the instrument’s resonance.
- String Care: Wipe down the strings after each playing session to remove sweat and oils, which can corrode the strings and diminish their sound quality. Consider using a string cleaner specifically designed for violins.
- Proper Storage: Store the violin in a case when not in use to protect it from dust, humidity, and temperature fluctuations. Extreme conditions can cause the wood to warp or crack, affecting the instrument’s sound and structural integrity.
- Humidity Control: Maintain a stable humidity level in the violin’s storage environment. Use a humidifier in dry climates to prevent the wood from drying out and cracking, and a dehumidifier in humid climates to prevent excessive moisture buildup.
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the violin for any signs of damage, such as cracks, loose seams, or warping. Address any issues promptly to prevent them from escalating and affecting the instrument’s sound.
- Professional Servicing: Schedule regular checkups with a qualified luthier to ensure the violin is in optimal condition. A luthier can assess the instrument’s setup, make necessary adjustments, and perform repairs as needed.
By incorporating these maintenance practices into your routine, you can extend the lifespan of your violin and ensure it continues to produce its best possible sound for years to come.
10. How Does Streetsounds.net Enhance the Experience of Exploring Violin Sounds?
Streetsounds.net offers a rich library of sounds, articles, and a community for those passionate about violin sounds. It provides resources and inspiration for musicians and sound enthusiasts looking to deepen their understanding and appreciation.
At streetsounds.net, we understand the passion for violin sounds and are dedicated to enhancing your experience in exploring this rich sonic landscape. Our platform offers a wealth of resources and opportunities for musicians, sound enthusiasts, and anyone looking to deepen their understanding and appreciation of violin sounds.
- Extensive Sound Library: Explore our extensive library of high-quality violin sounds, curated from various sources and styles. Whether you’re seeking the warm tones of a classical violin, the edgy sounds of an electric violin, or the unique textures of experimental violin techniques, you’ll find a diverse selection to inspire your creativity.
- Informative Articles and Tutorials: Delve into our collection of informative articles and tutorials that cover various aspects of violin sounds. From the physics of sound production to the history of violin making, from advanced playing techniques to sound design tips, our content is designed to educate and empower you on your sonic journey.
- Community Forum: Connect with fellow violin enthusiasts, musicians, and sound professionals in our vibrant community forum. Share your experiences, ask questions, exchange ideas, and collaborate on projects. Our community is a supportive space where you can learn from others and contribute your knowledge to the collective.
- Artist Spotlights: Discover inspiring stories and interviews with talented violinists and sound artists who are pushing the boundaries of violin sounds. Learn about their creative processes, techniques, and inspirations, and gain insights into the diverse world of violin music.
- Exclusive Content and Resources: Unlock exclusive content and resources, such as sample packs, presets, and sound design tools, available only to our members. These resources can help you create your unique violin sounds and elevate your musical projects.
Whether you’re a seasoned violinist, a budding sound designer, or simply a curious listener, streetsounds.net is your gateway to a world of violin sounds. Join our community today and embark on a sonic adventure!
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Violin Sounds
Here are some frequently asked questions about how violins make sound, covering various aspects from instrument components to maintenance and sound optimization.
1. What is the primary factor that causes a violin to produce sound?
The vibration of the strings, initiated by bowing or plucking, is the primary factor. These vibrations are then amplified and shaped by the violin’s body and other components.
2. How does the bridge contribute to the sound of a violin?
The bridge transfers the vibrations from the strings to the body of the violin, playing a vital role in amplifying and shaping the sound.
3. Why are f-holes important in a violin?
F-holes allow the sound to project from the violin’s body, influencing the instrument’s resonance and tonal qualities.
4. Can the type of wood used in a violin affect its sound?
Yes, different types of wood have varying densities and resonance characteristics, which can significantly impact the violin’s overall sound.
5. How often should violin strings be changed to maintain good sound quality?
Violin strings should be changed every 3-6 months, depending on how frequently the instrument is played, to maintain optimal sound quality.
6. What is the role of rosin in violin playing?
Rosin provides the necessary friction between the bow hair and strings, enabling vibration and sound production.
7. How does humidity affect the sound of a violin?
Extreme humidity levels can cause the wood to warp or crack, negatively impacting the violin’s sound and structural integrity.
8. What are some common signs that a violin needs professional maintenance?
Common signs include cracks, loose seams, buzzing sounds, and difficulty tuning or maintaining pitch.
9. How can a violinist experiment with different sounds on their instrument?
Violinists can experiment with different strings, bows, rosin types, and bowing techniques to explore the instrument’s full range of tonal possibilities.
10. How does streetsounds.net help musicians explore and enhance violin sounds?
Streetsounds.net offers a rich library of violin sounds, informative articles, a community forum, and exclusive resources to help musicians deepen their understanding and appreciation of violin sounds.
Ready to explore the world of street sounds and elevate your music? Visit streetsounds.net today!
Address: 726 Broadway, New York, NY 10003, United States
Phone: +1 (212) 998-8550
Website: streetsounds.net