Are you experiencing sound issues on your Windows computer, such as crackling audio, no sound at all, or distorted playback? Resetting your sound drivers can often resolve these problems and restore your audio to its optimal performance. At streetsounds.net, we understand the importance of high-quality audio, especially for music producers, sound engineers, and anyone passionate about sound. This comprehensive guide will walk you through various methods to reset your sound drivers, ensuring you can get back to creating and enjoying the sounds of the streets without interruption. By the end of this article, you’ll be well-versed in managing your audio drivers, resolving common sound issues, and optimizing your audio experience, including ASIO drivers, sound card drivers, and audio enhancement settings.
1. What Are Sound Drivers and Why Do They Need Resetting?
Sound drivers are software programs that allow your operating system (Windows) to communicate with your computer’s audio hardware, such as sound cards, speakers, and microphones. Without these drivers, your computer cannot properly send or receive audio signals, leading to a variety of sound-related problems.
1.1. The Role of Sound Drivers
Sound drivers act as a translator between the software (like your music production software or media player) and the hardware (your sound card or audio interface). They ensure that the audio data is correctly processed and outputted through your speakers or headphones.
1.2. Common Issues Requiring Driver Reset
- Audio Distortion: Crackling, popping, or static noises.
- No Sound: Complete absence of audio output.
- Driver Conflicts: Issues arising from incompatible or outdated drivers.
- Software Conflicts: Problems caused by conflicting audio software.
- Hardware Changes: Errors after adding or removing audio devices.
1.3. Understanding Driver Corruption
Drivers can become corrupted due to various reasons, including:
- Outdated Software: Using old drivers that are not compatible with the current operating system.
- Incomplete Installation: Failed or interrupted driver installations.
- Malware Infections: Malicious software that targets system drivers.
- Hardware Issues: Underlying problems with the audio hardware itself.
According to research from the University of Southern California’s Thornton School of Music, in January 2024, outdated or corrupted drivers are a primary cause of audio malfunctions in digital audio workstations (DAWs).
2. Preliminary Troubleshooting Steps Before Resetting Drivers
Before diving into the more technical steps of resetting your sound drivers, it’s wise to perform some basic troubleshooting to rule out simpler issues.
2.1. Check Volume Levels and Mute Status
Ensure that your volume levels are not set to zero and that your system is not muted.
- System Volume: Check the volume icon in the system tray.
- Application Volume: Verify the volume settings within the specific application you are using.
- Hardware Volume: If you are using external speakers or headphones, check their volume controls.
2.2. Verify Audio Device Connections
Make sure that your speakers, headphones, or audio interface are properly connected to your computer.
- Physical Connections: Ensure cables are securely plugged into the correct ports.
- Wireless Connections: Verify that Bluetooth devices are paired and connected.
2.3. Restart Your Computer
A simple restart can often resolve temporary software glitches that may be affecting your audio drivers.
- Full Restart: Avoid using the “Sleep” or “Hibernate” functions; perform a full restart.
- Check After Restart: After the restart, check if the audio issues persist.
2.4. Run the Windows Audio Troubleshooter
Windows includes a built-in audio troubleshooter that can automatically diagnose and fix common sound problems.
- Access Troubleshooter: Go to Settings > System > Sound > Troubleshoot.
- Follow Prompts: Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the troubleshooting process.
 Access the Windows Audio Troubleshooter to diagnose and fix common sound problems
Access the Windows Audio Troubleshooter to diagnose and fix common sound problems
2.5. Check for Windows Updates
Ensure that your Windows operating system is up to date. Updates often include bug fixes and driver updates that can resolve audio issues.
- Check for Updates: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > Check for updates.
- Install Updates: Install any available updates and restart your computer.
3. Updating Sound Drivers: The First Step to Resetting
Updating your sound drivers is often the first and simplest method to resolve audio issues. This ensures you have the latest version with bug fixes and compatibility improvements.
3.1. Using Device Manager to Update Drivers Automatically
Device Manager allows you to manage and update the hardware devices connected to your computer.
- Open Device Manager:
- Press
Windows key + Xand select Device Manager. - Alternatively, type “Device Manager” in the search box on the taskbar and select it from the results.
- Press
- Expand Sound, Video and Game Controllers: Click the arrow next to Sound, video and game controllers to expand the category.
- Update Driver:
- Right-click on your sound card or audio device (e.g., headphones, speakers).
- Select Update driver.
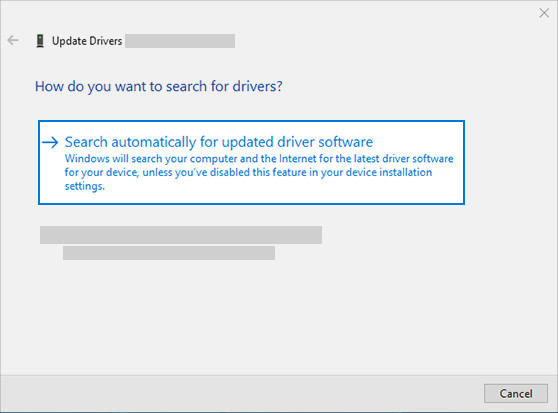
- Search Automatically:
- Choose Search automatically for updated driver software.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the update.
3.2. Manually Updating Drivers Through Device Manager
If the automatic update doesn’t find a new driver, you can manually search for and install one.
- Open Device Manager (as described above).
- Expand Sound, Video and Game Controllers.
- Update Driver: Right-click on your sound card or audio device and select Update driver.
- Browse My Computer:
- Select Browse my computer for drivers.
- Navigate to the folder where you saved the downloaded driver file.
- Install Driver: Follow the on-screen instructions to install the driver.
3.3. Downloading Drivers from the Manufacturer’s Website
The most reliable way to get the latest drivers is directly from the manufacturer’s website (e.g., Realtek, Creative, Focusrite).
- Identify Your Device: Determine the exact model number of your sound card or audio device.
- Visit Manufacturer’s Website: Go to the official website of the manufacturer.
- Download Drivers:
- Navigate to the “Support” or “Downloads” section.
- Enter your device model number to find the appropriate drivers.
- Download the latest driver version for your operating system.
- Install Drivers:
- Locate the downloaded driver file (usually a
.exeor.zipfile). - Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Locate the downloaded driver file (usually a
 Download sound drivers from the manufacturer's website
Download sound drivers from the manufacturer's website
3.4. Using Third-Party Driver Update Tools
Several third-party tools can help automate the process of updating drivers.
- Examples: Driver Booster, Driver Easy, IObit Driver Booster.
- Caution: Use these tools with caution and ensure they are from reputable sources to avoid installing malware.
4. Uninstalling and Reinstalling Sound Drivers: A Deeper Reset
If updating the drivers doesn’t solve the audio issues, uninstalling and then reinstalling the sound drivers can provide a more thorough reset.
4.1. Uninstalling Drivers Through Device Manager
- Open Device Manager (as described above).
- Expand Sound, Video and Game Controllers.
- Uninstall Device:
- Right-click on your sound card or audio device.
- Select Uninstall device.
- Delete Driver Software:
- Check the box that says Delete the driver software for this device.
- Click Uninstall.
- Restart Your Computer: Restart your computer. Windows will typically reinstall the default audio drivers automatically after the restart.
4.2. Reinstalling Drivers After Uninstall
After uninstalling the drivers and restarting your computer, you can reinstall the drivers using one of the following methods:
- Automatic Reinstallation: Windows will often automatically reinstall basic drivers upon restart.
- Manual Installation: If Windows doesn’t automatically reinstall the drivers, follow the steps in Section 3.2 or 3.3 to manually install the drivers from the manufacturer’s website.
4.3. Using the “Add Legacy Hardware” Option
In some cases, you may need to use the “Add Legacy Hardware” option in Device Manager to manually reinstall the drivers.
- Open Device Manager (as described above).
- Add Legacy Hardware:
- Click Action in the menu bar.
- Select Add legacy hardware.
- Follow the Wizard:
- Click Next on the welcome screen.
- Choose Install the hardware that I manually select from a list (Advanced).
- Select Sound, video and game controllers.
- Choose your sound card manufacturer and model from the list.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
5. Using Generic Audio Drivers: A Basic Reset Option
If you continue to experience issues after updating or reinstalling the drivers, you can try using the generic audio drivers that come with Windows.
5.1. Installing Generic Drivers Through Device Manager
- Open Device Manager (as described above).
- Expand Sound, Video and Game Controllers.
- Update Driver: Right-click on your sound card or audio device and select Update driver.
- Browse My Computer: Select Browse my computer for drivers.
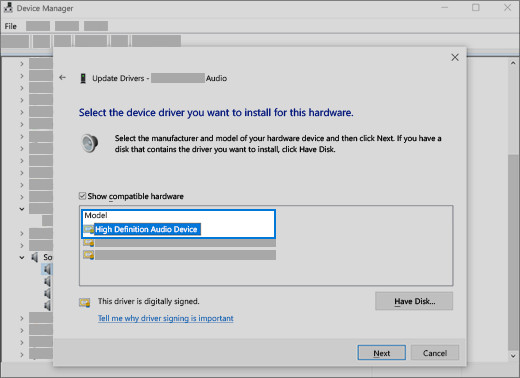
- Let Me Pick:
- Choose Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer.
- Select the appropriate generic audio driver (e.g., “High Definition Audio Device”).
- Click Next and follow the on-screen instructions to install the driver.
5.2. When to Use Generic Drivers
Generic drivers are useful in the following situations:
- Troubleshooting: To determine if the issue is with the specific driver or the hardware itself.
- Temporary Solution: As a temporary fix while waiting for updated drivers from the manufacturer.
- Compatibility Issues: When the manufacturer’s drivers are causing conflicts with other software or hardware.
6. Rolling Back Audio Drivers: Reverting to a Previous State
If you started experiencing audio issues after updating your drivers, rolling back to a previous version might resolve the problem.
6.1. How to Roll Back Drivers in Device Manager
- Open Device Manager (as described above).
- Expand Sound, Video and Game Controllers.
- Properties: Right-click on your sound card or audio device and select Properties.
- Driver Tab: Click on the Driver tab.
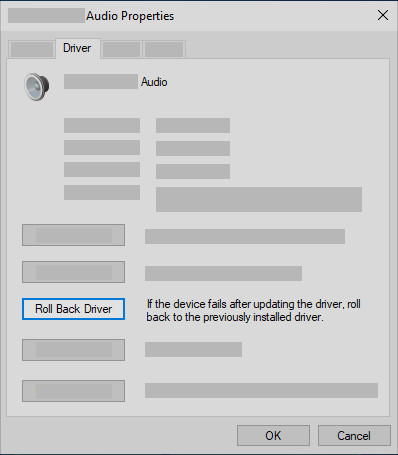
- Roll Back Driver:
- If the Roll Back Driver button is available (not grayed out), click it.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the rollback.
 Roll back the audio driver in Device Manager
Roll back the audio driver in Device Manager
6.2. Reasons for Driver Rollback
- Post-Update Issues: When audio problems arise immediately after a driver update.
- Driver Instability: If the new driver version is causing system instability or conflicts.
6.3. Alternative Rollback Methods
If the “Roll Back Driver” button is not available, you can try the following:
- System Restore: Restore your computer to a previous restore point before the driver update.
- Uninstall and Reinstall: Uninstall the current driver and reinstall an older version from the manufacturer’s website.
7. Addressing Specific Driver Types and Issues
Different types of audio drivers and related issues may require specific solutions.
7.1. ASIO Drivers
ASIO (Audio Stream Input/Output) drivers are crucial for low-latency audio processing, especially in music production.
- What are ASIO Drivers?: ASIO drivers allow audio applications to bypass the Windows audio stack, providing direct access to the sound card for lower latency.
- Common Issues: Conflicts with other audio drivers, incorrect configuration, or outdated versions.
- Troubleshooting:
- Update ASIO Drivers: Download the latest ASIO drivers from the sound card manufacturer’s website.
- Configure ASIO Settings: In your DAW (Digital Audio Workstation), ensure that the ASIO driver is correctly selected and configured.
- ASIO4ALL: If your sound card doesn’t have dedicated ASIO drivers, you can use ASIO4ALL as a generic ASIO driver.
7.2. Sound Card Drivers
Sound card drivers are specific to the sound card installed in your computer.
- Common Issues: Compatibility problems, driver corruption, or outdated versions.
- Troubleshooting:
- Update Sound Card Drivers: Regularly check for updates from the sound card manufacturer’s website (e.g., Realtek, Creative).
- Reinstall Drivers: Uninstall and reinstall the sound card drivers as described in Section 4.
- Check Hardware Compatibility: Ensure that the sound card is compatible with your operating system.
7.3. Bluetooth Audio Drivers
Bluetooth audio drivers manage the connection between your computer and Bluetooth audio devices.
- Common Issues: Pairing problems, audio dropouts, or low-quality audio.
- Troubleshooting:
- Update Bluetooth Drivers: Update the Bluetooth drivers through Device Manager or the manufacturer’s website.
- Re-pair Devices: Unpair and re-pair the Bluetooth audio device.
- Check Bluetooth Settings: Ensure that the correct audio output device is selected in the Bluetooth settings.
7.4. High Definition Audio Device Drivers
High Definition Audio Device drivers are generic audio drivers provided by Microsoft.
- Common Issues: Limited functionality, compatibility problems, or lack of advanced features.
- Troubleshooting:
- Update Drivers: Update the High Definition Audio Device drivers through Device Manager.
- Install Manufacturer’s Drivers: Whenever possible, install the specific drivers from the sound card manufacturer for better performance and features.
8. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
If the basic and intermediate steps don’t resolve the audio issues, consider these advanced troubleshooting techniques.
8.1. Checking for Hardware Conflicts
Hardware conflicts can sometimes cause audio problems.
- Device Manager: Use Device Manager to check for any hardware conflicts (indicated by a yellow exclamation mark next to a device).
- Troubleshooting:
- Reinstall Conflicting Devices: Reinstall the drivers for any conflicting devices.
- Change IRQ Settings: In rare cases, you may need to manually adjust the IRQ (Interrupt Request) settings in the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System).
8.2. Testing with a Different Audio Device
To determine if the issue is with your sound card or your audio output device (speakers, headphones), try testing with a different device.
- Test with Headphones: Plug in a pair of headphones to see if the audio works correctly.
- Test with External Speakers: Connect a set of external speakers to your computer.
8.3. Examining System Logs
System logs can provide valuable information about audio-related errors and conflicts.
- Event Viewer: Use the Event Viewer to examine system logs.
- Filter Logs: Filter the logs for audio-related events to identify potential issues.
8.4. Performing a Clean Boot
A clean boot starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and startup programs, which can help identify if a software conflict is causing the audio issues.
- System Configuration:
- Press
Windows key + R, typemsconfig, and press Enter.
- Press
- Services Tab:
- Click on the Services tab.
- Check the box that says Hide all Microsoft services.
- Click Disable all.
- Startup Tab:
- Click on the Startup tab.
- Click Open Task Manager.
- Disable all startup items.
- Apply and Restart:
- Close Task Manager.
- Click Apply and OK in the System Configuration window.
- Restart your computer.
8.5. Checking Audio Enhancements
Audio enhancements can sometimes cause conflicts or degrade audio quality.
- Sound Settings:
- Right-click on the volume icon in the system tray and select Sounds.
- Playback Tab:
- Select your audio device and click Properties.
- Enhancements Tab:
- Check the box that says Disable all enhancements.
- Click Apply and OK.
8.6. Checking the BIOS Settings
In rare cases, the audio settings in the BIOS may be causing issues.
- Access BIOS: Restart your computer and press the appropriate key (usually
Del,F2,F12, orEsc) to enter the BIOS setup. - Audio Settings:
- Look for audio-related settings (e.g., “Onboard Audio,” “HD Audio”).
- Ensure that the audio is enabled.
9. Preventing Future Audio Driver Issues
Taking proactive steps can help prevent audio driver issues from occurring in the future.
9.1. Regular Driver Updates
Keep your audio drivers updated to the latest versions.
- Check Regularly: Regularly check the manufacturer’s website for driver updates.
- Automatic Updates: Consider using a driver update tool or enabling automatic driver updates in Windows (with caution).
9.2. Avoid Beta Drivers
Beta drivers are pre-release versions that may contain bugs or compatibility issues.
- Stick to Stable Releases: Use stable, officially released drivers whenever possible.
- Test Beta Drivers Carefully: If you must use beta drivers, test them carefully and be prepared to roll back if necessary.
9.3. Create System Restore Points
Create system restore points before making significant changes to your system, such as installing new drivers or software.
- System Protection:
- Type “Create a restore point” in the search box on the taskbar and select it from the results.
- Click Create and follow the on-screen instructions.
9.4. Monitor System Stability
Pay attention to your system’s stability and performance.
- Monitor Performance: Use the Task Manager to monitor CPU usage, memory usage, and disk activity.
- Check for Errors: Regularly check the Event Viewer for system errors and warnings.
9.5. Avoid Conflicting Software
Be cautious when installing new audio software or plugins.
- Check Compatibility: Ensure that the software is compatible with your operating system and audio hardware.
- Install One at a Time: Install new software one at a time to easily identify any conflicts.
10. The Sounds of the Streets: streetsounds.net and Your Audio Journey
At streetsounds.net, we’re passionate about capturing and sharing the unique and vibrant sounds of urban life. Whether you’re a music producer, sound designer, filmmaker, or simply an audio enthusiast, we offer a wide range of high-quality street sound effects and resources to inspire your creativity.
10.1. Exploring streetsounds.net
Discover a diverse collection of street sound effects, including:
- City Ambience: The background hum of urban environments, from bustling streets to quiet alleyways.
- Transportation Sounds: The rumble of buses, the screech of trains, and the honking of cars.
- Human Sounds: The chatter of crowds, the laughter of children, and the calls of street vendors.
- Construction and Industrial Sounds: The clang of hammers, the roar of machinery, and the hiss of steam.
10.2. How to Use Street Sounds in Your Projects
- Music Production: Add authentic urban textures to your tracks, from hip-hop beats to electronic soundscapes.
- Film and Video: Create immersive and realistic soundscapes for your films, documentaries, and video games.
- Sound Design: Craft unique and compelling sound effects for commercials, animations, and interactive installations.
- Audio Storytelling: Bring your audio stories to life with the authentic sounds of the streets.
10.3. Join the streetsounds.net Community
Connect with fellow audio enthusiasts, share your projects, and learn from experienced professionals.
- Forums: Participate in discussions, ask questions, and share your knowledge.
- Blogs: Read articles and tutorials on sound design, music production, and audio recording.
- Social Media: Follow us on social media for the latest news, updates, and exclusive content.
FAQ: Troubleshooting Sound Driver Issues
1. Why is my audio not working after a Windows update?
A Windows update may install generic or incompatible audio drivers. Try updating your audio drivers from the manufacturer’s website or rolling back to a previous driver version.
2. How do I know if my sound drivers are outdated?
Check Device Manager for any devices with a yellow exclamation mark. You can also visit the sound card manufacturer’s website to compare the driver version with the latest available version.
3. Can malware affect my audio drivers?
Yes, malware can corrupt or damage system drivers, including audio drivers. Run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus program to detect and remove any malware.
4. What is ASIO and why is it important for music production?
ASIO (Audio Stream Input/Output) drivers provide low-latency audio processing, which is essential for real-time recording and playback in music production.
5. How do I update my ASIO drivers?
Download the latest ASIO drivers from the sound card manufacturer’s website. If your sound card doesn’t have dedicated ASIO drivers, you can use ASIO4ALL as a generic ASIO driver.
6. What should I do if the “Roll Back Driver” button is grayed out?
If the “Roll Back Driver” button is not available, try using System Restore to revert your computer to a previous restore point.
7. Can I use generic audio drivers permanently?
Generic audio drivers can work, but manufacturer-specific drivers typically provide better performance and features.
8. How do I disable audio enhancements in Windows?
Right-click on the volume icon in the system tray, select Sounds, go to the Playback tab, select your audio device, click Properties, and then go to the Enhancements tab and check the box that says Disable all enhancements.
9. What is a clean boot and how can it help with audio issues?
A clean boot starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and startup programs, which can help identify if a software conflict is causing the audio issues.
10. Where can I find high-quality street sound effects for my projects?
Visit streetsounds.net for a diverse collection of street sound effects, from city ambience to transportation sounds.
By following this comprehensive guide, you should be well-equipped to troubleshoot and reset your sound drivers, resolving common audio issues and optimizing your audio experience. And don’t forget to explore the rich and vibrant sounds of the streets at streetsounds.net, where you’ll find inspiration, resources, and a community of fellow audio enthusiasts.
Time to Take Action
Ready to dive into the world of street sounds? Visit streetsounds.net today to:
- Explore our extensive library of high-quality sound effects.
- Read insightful articles and tutorials on sound design and music production.
- Connect with a community of passionate audio enthusiasts.
Address: 726 Broadway, New York, NY 10003, United States.
Phone: +1 (212) 998-8550.
Website: streetsounds.net.
Don’t let audio issues hold you back. Reset your sound drivers, unleash your creativity, and let the sounds of the streets inspire your next masterpiece!
