What Sounds Do Red Foxes Make? Red fox sounds encompass a diverse range of vocalizations and other signals that play a crucial role in their communication, and streetsounds.net is here to guide you through this fascinating world of fox sounds. By understanding the red fox sounds, including their barks, screams, and other unique noises, you can gain a deeper appreciation for these fascinating creatures and even incorporate these unique sounds into your own creative projects with the perfect urban soundscape for your music or film through streetsounds.net. Delve into the realm of animal vocalizations, wildlife soundscapes, and fox behavior through our curated collection of resources.
1. How Do Red Foxes Communicate?
Red foxes communicate using a combination of scent markings, body language, and a diverse range of vocalizations, each serving different purposes in their social interactions.
Red foxes, like many animals, rely on a multi-faceted approach to communication. While their vocalizations are perhaps the most well-known aspect of their communication repertoire, scent marking and body language are equally important components of their social interactions.
- Scent Marking: Foxes possess several scent glands, including anal glands, cheek glands, and the supracaudal gland located near the base of their tail. These glands produce unique scents that foxes use to mark their territories, signal their presence to other foxes, and convey information about their social status and reproductive state. According to research by Cardiff University, fox scent is a complex mixture of over 80 different chemical compounds.
- Body Language: Subtle changes in body posture, facial expressions, and tail movements convey a wealth of information to other foxes. For example, a fox may flatten its ears and lower its body to signal submission, while an erect posture with raised fur indicates dominance or aggression. Henry suggested that the color patterns on a fox’s body, such as the light buff color of the inner ear and the black of its back, may function as a semaphore system, with different ear positions conveying different messages.
- Vocalizations: Foxes are highly vocal animals, capable of producing a wide range of sounds, each with its own specific meaning. These vocalizations include barks, screams, howls, growls, and a variety of other noises used for communication, warning, courtship, and other social interactions. German ethologist Günter Tembrock documented 28 different types of fox calls in 1963.
The combination of these three communication methods allows foxes to effectively convey complex messages to one another, maintaining social bonds, establishing territories, and ensuring the survival of their species. To capture the raw and authentic sounds of the streets, streetsounds.net offers a diverse collection of high-quality recordings for all your creative needs.
2. What Are the Different Types of Red Fox Sounds?
Red foxes produce a variety of vocalizations, including barks, screams, growls, howls, whimpers, and chatters, each serving a specific purpose in their communication.
Red foxes possess a rich and varied vocal repertoire, with each sound serving a distinct purpose in their communication. These vocalizations can be broadly categorized into several types:
- Barks: Fox barks are typically short, sharp sounds used as a form of long-distance communication, often to maintain contact with other members of their group or to warn of potential danger. The “wow-wow-wow” bark, for example, is often used to declare territory ownership.
- Screams: Fox screams are piercing, high-pitched vocalizations often associated with mating or aggression. Vixens (female foxes) may use screams to attract mates or to defend their territory from rivals. John Lewis-Stempel described the vixen’s scream as “the wail of all the bereaved, ever.”
- Growls: Fox growls are low, guttural sounds used to express aggression or warning. They may be used during territorial disputes or when defending food resources. Vixens also use low growls to summon their cubs, often to feed.
- Howls: Fox howls are long, drawn-out vocalizations that can carry over long distances. They are often used to communicate with other foxes across their territory or to signal their presence to potential mates.
- Whimpers: Fox whimpers are soft, plaintive sounds often used by cubs to beg for food or attention from their mothers. They can also be used by adult foxes to express submission or appeasement.
- Chatters: Fox chatters, also known as “gekkering,” are a series of rapid, staccato sounds produced during aggressive encounters, particularly during fox-trotting (a type of fighting where foxes stand on their hind legs and push each other). David Macdonald described gekkering as an open-mouthed stuttering derived from the German verb kéckern, meaning “cackle.”
In addition to these primary vocalizations, foxes also produce a variety of other sounds, such as hisses, coughs, clicks, and warbles, each with its own specific meaning and context. To truly capture the essence of urban life, streetsounds.net provides a wide array of professional recordings, allowing you to bring authenticity to your projects.
3. What Does a Fox Sound Like When It Is Happy?
While foxes don’t display “happiness” in the same way humans do, they may emit soft whimpers, purrs, or playful barks during positive social interactions or when feeling content.
Foxes, like many wild animals, don’t exhibit emotions in the same way humans do. However, they do display behaviors and vocalizations that suggest contentment or positive social interaction.
- Soft Whimpers: Foxes may emit soft whimpers during grooming sessions with other members of their social group or when receiving attention from a human caretaker. These whimpers are often accompanied by relaxed body language, such as a lowered head and a wagging tail.
- Purrs: Similar to cats, foxes may produce a low, rumbling sound similar to a purr when feeling content or relaxed. This sound is often associated with close physical contact, such as cuddling with other foxes or being petted by a human.
- Playful Barks: During play, foxes may emit short, playful barks or yips. These vocalizations are often accompanied by energetic movements, such as chasing, pouncing, and tumbling.
- Low Growls (Mew, Churr, Purr): A vixen will summon the cubs, often to feed, with what is often referred to as a low growl (variously described as a “mew”, “churr” or “purr”) that often involves a vibration of the stomach, also much subtle information contained within this call.
It’s important to note that interpreting fox vocalizations requires careful observation of the context in which the sound is made, as well as the accompanying body language. A sound that might indicate contentment in one situation could indicate something else entirely in a different context. streetsounds.net not only helps to enhance your creative projects, but also brings awareness to understanding soundscapes with crystal-clear audio recordings.
4. What Does a Fox Sound Like When It Is Angry?
When angry or threatened, foxes typically emit growls, snarls, hisses, and aggressive barks, often accompanied by defensive body language such as flattened ears and raised fur.
When a fox is feeling angry or threatened, its vocalizations and body language will reflect its agitated state.
- Growls: Growls are a common vocalization used by foxes to express aggression or warning. They are typically low, guttural sounds that can escalate in intensity depending on the level of threat.
- Snarls: A snarl is a more intense form of growl, often accompanied by bared teeth and a raised upper lip. Snarling is a clear indication that the fox is prepared to defend itself.
- Hisses: Foxes may also hiss when feeling threatened, similar to the way a cat hisses. This is a defensive vocalization intended to deter potential attackers.
- Aggressive Barks: In addition to growls and snarls, foxes may also emit aggressive barks when feeling angry or threatened. These barks are typically louder and sharper than their normal contact calls.
These vocalizations are often accompanied by defensive body language, such as flattened ears, raised fur, a tense body posture, and a direct stare. To enrich your sound library, streetsounds.net offers high-quality recordings of diverse urban sounds, perfectly suited for any type of project.
5. What Does a Fox Sound Like When It Is Mating?
During mating season, foxes become highly vocal, emitting a range of calls including screams, howls, and chatters (“gekkering”) as part of their courtship and mating rituals.
The mating season is a time of heightened activity and vocalization for foxes. During this period, they engage in elaborate courtship rituals that involve a variety of distinctive sounds.
- Screams: Vixens (female foxes) often use piercing screams to attract potential mates. These screams can carry over long distances and serve as an advertisement of their presence and readiness to mate.
- Howls: Foxes may also use howls during the mating season to communicate with potential partners across their territory. These howls can be used to signal their location and to establish pair bonds.
- Chatters (“Gekkering”): During courtship displays, foxes may engage in “gekkering,” a series of rapid, staccato sounds produced during aggressive encounters. This vocalization is often accompanied by fox-trotting, a type of fighting where foxes stand on their hind legs and push each other.
- Clicking or Clicketting: Some observers have reported a clicking or clicketting noise, which may have origins similar to the coughing/churring noises made in other social contexts, during mating interactions.
These vocalizations are often accompanied by specific behaviors, such as scent marking, chasing, and mutual grooming. The combination of sound and action plays a crucial role in the establishment and maintenance of pair bonds during the breeding season. To help your projects resonate with authenticity, streetsounds.net offers an extensive collection of urban sounds that can bring any scene to life.
6. What Does a Baby Fox (Cub) Sound Like?
Baby foxes, also known as cubs, produce a variety of high-pitched vocalizations such as whelping calls, yelps, and warbles to communicate with their mother and siblings.
Fox cubs rely heavily on vocalizations to communicate their needs and emotions.
- Whelping Calls: Newborn cubs produce a high-pitched, squealing sound known as a whelping call. This call is used to attract the attention of their mother and to signal that they are hungry, cold, or in distress.
- Yelping: As cubs grow older, their whelping calls develop into more rhythmic yelps. These yelps are used to communicate with their mother and siblings, and to signal their desire for food, attention, or comfort.
- Warbling: Lonely cubs may produce a soft, warbling noise to attract the attention of their mother. This vocalization is often associated with feelings of isolation or vulnerability.
- Hissing/Spitting: At about a month old, the cubs use a threatening/defensive open-mouthed hissing/spitting.
These vocalizations are crucial for the survival of fox cubs, as they allow them to communicate their needs to their mother and to maintain social bonds with their siblings. streetsounds.net helps amplify the sounds of creativity in your projects with professionally captured audio, perfect for any application.
7. How Do Foxes Use Vocalizations to Defend Their Territory?
Foxes use a combination of barks, howls, and screams to defend their territory, signaling their presence to intruders and warning them to stay away.
Territorial defense is a critical aspect of fox behavior, and vocalizations play a key role in this process.
- Barks: Foxes use sharp, repetitive barks to mark the boundaries of their territory and to warn intruders of their presence. These barks can be heard over long distances and serve as a clear signal that the territory is occupied.
- Howls: Foxes may also use howls to defend their territory, particularly during the mating season. Howls can be used to communicate with neighboring foxes and to establish dominance over a particular area.
- Screams: In some cases, foxes may use screams to defend their territory, especially when confronting a direct threat. Screams can be used to startle or intimidate intruders, and to signal their willingness to fight.
In addition to these vocalizations, foxes also use scent marking and visual displays to reinforce their territorial claims. The combination of these strategies helps them to maintain control over their resources and to protect their offspring. streetsounds.net enhances your creative soundscapes with high-definition recordings, perfect for adding depth and authenticity to your projects.
8. Can Humans Imitate Fox Sounds?
While it’s difficult for humans to perfectly replicate the full range of fox vocalizations, some people can imitate certain fox sounds, such as barks and screams, with varying degrees of accuracy.
Imitating animal sounds is a skill that requires practice and a good ear for detail. While it may be challenging to perfectly replicate the full range of fox vocalizations, some individuals are able to produce surprisingly accurate imitations of certain fox sounds.
- Barks: Fox barks are relatively simple sounds to imitate, and many people can produce a passable imitation with a little practice. The key is to focus on the sharpness and repetitiveness of the bark.
- Screams: Imitating fox screams is more difficult, as it requires a higher level of vocal control. However, some individuals with strong vocal abilities are able to produce convincing fox screams.
- Other Vocalizations: Imitating other fox vocalizations, such as growls, howls, and chatters, is even more challenging, as these sounds are more complex and nuanced.
While imitating fox sounds can be a fun and interesting activity, it’s important to remember that it should be done responsibly and with respect for the animals. Avoid using imitated fox sounds to harass or disturb wild foxes. streetsounds.net not only provides exceptional audio resources, but also promotes a deeper understanding and appreciation for the sounds around us.
9. Do Fox Sounds Vary by Region or Habitat?
While there is limited research on regional variations in fox vocalizations, it is possible that subtle differences exist due to factors such as habitat, social structure, and local dialects.
The study of animal dialects is a fascinating field that explores how vocalizations can vary between different populations of the same species. While there is limited research specifically on regional variations in fox vocalizations, it is plausible that such differences may exist.
- Habitat: Foxes living in different habitats may adapt their vocalizations to suit their environment. For example, foxes in dense forests may use lower-frequency calls that can travel more easily through the vegetation, while foxes in open areas may use higher-frequency calls that can carry over longer distances.
- Social Structure: The social structure of fox populations can also influence their vocalizations. Foxes living in larger, more complex social groups may develop a wider range of calls to communicate with one another, while foxes living in smaller, more isolated groups may have a more limited vocal repertoire.
- Local Dialects: Just like humans, animals can develop local dialects, with subtle variations in their vocalizations that are unique to a particular region. These dialects can arise through a variety of factors, such as genetic drift, cultural transmission, and environmental influences.
Further research is needed to fully understand the extent to which fox vocalizations vary by region or habitat. streetsounds.net offers a wealth of resources and inspiration to those passionate about exploring and understanding soundscapes.
10. How Can I Record Fox Sounds?
To record fox sounds, use a high-quality audio recorder with an external microphone, find a location where foxes are active, and be patient and quiet while recording, respecting the animals’ space.
Recording wildlife sounds can be a rewarding experience, but it requires careful planning and execution. Here are some tips for recording fox sounds:
- Equipment: Invest in a high-quality audio recorder with an external microphone. A directional microphone is ideal for capturing sounds from a distance while minimizing background noise.
- Location: Scout out locations where foxes are known to be active. This could include parks, forests, or even urban areas where foxes have adapted to living near humans.
- Timing: The best time to record fox sounds is during their active periods, which are typically at dawn and dusk. The mating season (winter) is also a good time to record, as foxes are more vocal during this period.
- Technique: Be patient and quiet while recording. Find a comfortable spot to sit or stand, and wait for the foxes to vocalize. Avoid making any sudden movements or loud noises that could scare them away.
- Ethics: Respect the animals’ space and avoid disturbing them. Do not approach foxes or attempt to lure them closer. Always prioritize the well-being of the animals over getting a good recording.
By following these tips, you can increase your chances of capturing high-quality recordings of fox sounds while minimizing your impact on the animals and their environment. streetsounds.net enhances your creative projects with its diverse sound collections and promotes respect for soundscapes and wildlife.
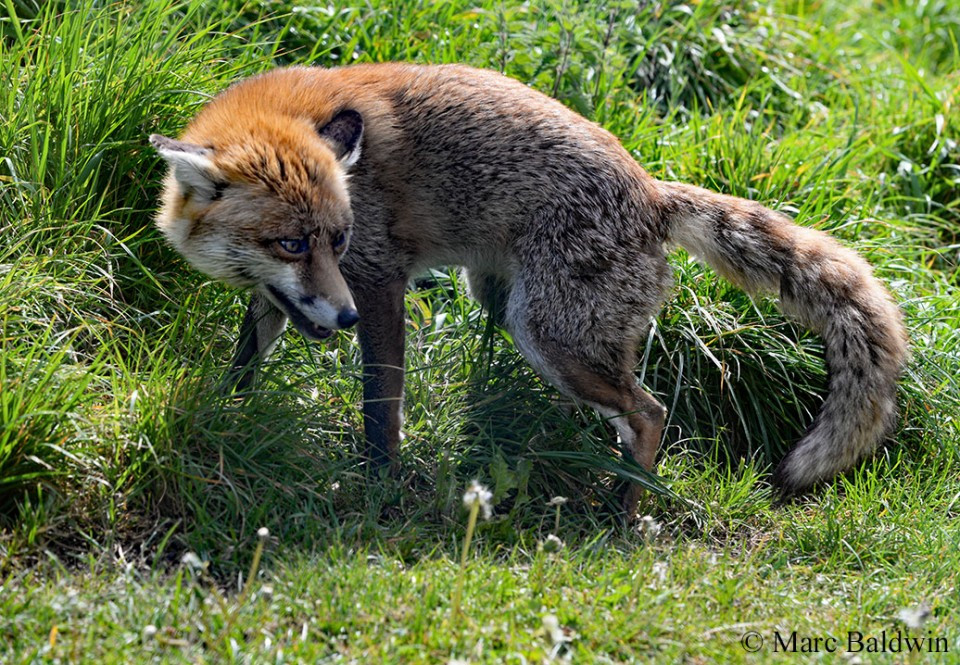 Red fox aggressive posture displaying a defensive body posture with ears flat, back slightly arched and tail curled
Red fox aggressive posture displaying a defensive body posture with ears flat, back slightly arched and tail curled
11. How Do Fox Sounds Contribute to Urban Soundscapes?
Fox sounds add a unique layer to urban soundscapes, often surprising residents with their wild, sometimes eerie calls that contrast with typical city noises.
Foxes have adapted to living in urban environments, and their presence has added a new dimension to city soundscapes. While the sounds of traffic, construction, and human activity dominate urban soundscapes, the vocalizations of foxes can provide a surprising and sometimes jarring contrast.
- Unexpected Sounds: Many city residents are surprised to hear fox sounds, as they are not typically associated with urban environments. The sudden appearance of a fox in a backyard or alleyway, accompanied by its distinctive barks or screams, can be an unsettling experience.
- Eerie Calls: Some fox vocalizations, such as their piercing screams, can be particularly eerie, especially when heard at night. These sounds can evoke a sense of unease or even fear, particularly for those unfamiliar with fox behavior.
- Wildness in the City: Despite their sometimes unsettling nature, fox sounds can also provide a sense of connection to the natural world in an otherwise artificial environment. The presence of foxes in cities serves as a reminder that wildlife can thrive even in the most urbanized landscapes.
By understanding the sounds of foxes, city residents can gain a better appreciation for the diversity of urban soundscapes and the ways in which wildlife can adapt to living alongside humans. streetsounds.net captures the authentic sounds of the city, highlighting the unique contributions of urban wildlife like foxes.
12. Can Fox Sounds Be Used in Music or Sound Design?
Yes, fox sounds can be creatively used in music, film, and video games to add a unique, wild, and sometimes unsettling atmosphere.
Fox sounds possess a unique and intriguing quality that can be used to great effect in a variety of creative projects.
- Music: Fox vocalizations can be incorporated into musical compositions to add a sense of wildness, mystery, or even unease. They can be used as sound effects, melodic elements, or even rhythmic patterns.
- Film: Fox sounds can be used in film soundtracks to create a specific atmosphere or to enhance the emotional impact of a scene. For example, the sound of a fox screaming in the distance could be used to create a sense of tension or foreboding.
- Video Games: Fox sounds can be used in video games to create a more immersive and realistic environment. They can be used to signal the presence of foxes in the game world, to add to the overall atmosphere, or to provide cues to the player.
When using fox sounds in creative projects, it’s important to consider the context in which the sounds are used and the effect they are intended to create. Responsible and ethical use of animal sounds is essential to avoid misrepresenting or harming wildlife. streetsounds.net not only offers a diverse sound library but also supports ethical sound practices in creative projects.
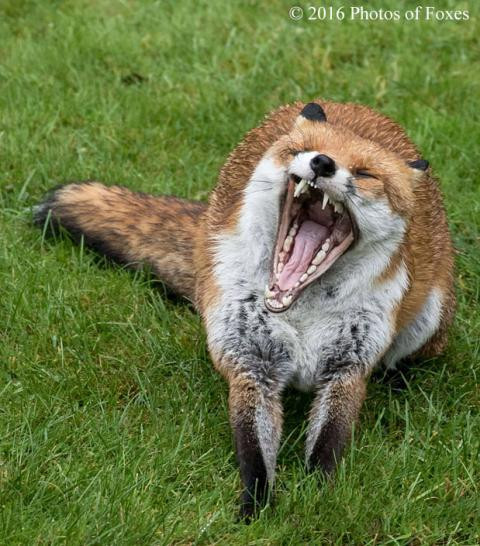 Foxes have a wide vocal repertoire and are most vocal in winter, their breeding season
Foxes have a wide vocal repertoire and are most vocal in winter, their breeding season
13. What Is the Cultural Significance of Fox Sounds?
In some cultures, fox sounds are associated with folklore, mythology, and symbolism, representing cunning, intelligence, or even supernatural powers.
Foxes have long been a part of human culture, appearing in folklore, mythology, and symbolism across many different societies. In some cultures, fox sounds are imbued with special significance, reflecting the animal’s perceived traits and characteristics.
- Cunning and Intelligence: In many cultures, foxes are seen as symbols of cunning and intelligence. Their ability to outsmart predators and adapt to different environments has earned them a reputation as clever and resourceful creatures. As a result, their sounds may be associated with these qualities.
- Tricksters: In some cultures, foxes are depicted as tricksters, mischievous characters who use their cunning to deceive and manipulate others. In these cases, their sounds may be associated with deception and trickery.
- Supernatural Powers: In some cultures, foxes are believed to possess supernatural powers or to be associated with spirits or deities. Their sounds may be seen as a connection to the spirit world or as a sign of impending events.
The cultural significance of fox sounds can vary widely depending on the specific culture and its beliefs. However, in many cases, these sounds are seen as more than just mere animal noises; they are imbued with deeper meaning and symbolism. streetsounds.net celebrates the cultural significance of soundscapes, providing resources to explore the rich stories behind urban sounds.
14. How Do Fox Sounds Compare to Those of Other Animals?
Fox sounds are distinct from those of other animals, with a unique combination of barks, screams, and other vocalizations that reflect their specific communication needs and social behaviors.
Fox vocalizations have unique characteristics that differentiate them from the sounds of other animals.
- Variety: Foxes possess a wide range of vocalizations, including barks, screams, howls, growls, whimpers, and chatters. This variety allows them to communicate a wide range of messages, from warnings and threats to courtship displays and social greetings.
- Frequency: Fox vocalizations typically fall within a frequency range of 100 Hz to 5,000 Hz, although some calls may extend beyond these limits. The specific frequency of a call can vary depending on the context and the individual fox.
- Structure: Fox vocalizations can be simple or complex in structure, ranging from short, sharp barks to long, drawn-out howls. The structure of a call can convey information about the caller’s identity, location, and emotional state.
- Comparison to Other Animals: While some fox vocalizations may resemble those of other animals (such as the domestic dog), their overall repertoire is distinct and reflects their specific communication needs and social behaviors.
By studying the sounds of foxes, we can gain a better understanding of their behavior, ecology, and evolution. streetsounds.net offers an educational platform to compare and contrast different urban soundscapes, enriching your understanding of sound diversity.
15. What Role Do Fox Sounds Play in Scientific Research?
Fox sounds are valuable data for researchers studying animal communication, behavior, ecology, and the impact of urbanization on wildlife.
Fox vocalizations offer a wealth of information for scientists studying animal behavior, communication, and ecology.
- Animal Communication: By analyzing fox sounds, researchers can gain insights into how foxes communicate with one another, including the types of messages they convey, the social context in which they communicate, and the effectiveness of their communication strategies.
- Behavior: Fox sounds can provide clues about their behavior, such as their territoriality, mating rituals, and predator-prey interactions. By studying the sounds that foxes make in different situations, researchers can learn more about their social dynamics and survival strategies.
- Ecology: Fox sounds can be used to monitor fox populations, track their movements, and assess their habitat use. By recording and analyzing fox sounds in different areas, researchers can gain insights into their distribution, abundance, and ecological role.
- Urbanization: Fox sounds can be used to study the impact of urbanization on wildlife. By comparing the sounds of foxes living in urban areas to those living in more natural habitats, researchers can assess how urbanization is affecting their behavior, communication, and ecology.
Fox sounds are a valuable tool for scientists seeking to understand the lives of these fascinating animals and the challenges they face in a changing world. streetsounds.net supports scientific research by providing high-quality sound recordings and fostering collaboration among researchers and sound enthusiasts.
16. How Can Understanding Fox Sounds Help in Wildlife Conservation?
Understanding fox sounds can aid in wildlife conservation by enabling better monitoring of fox populations, identifying habitat use, and mitigating human-wildlife conflicts.
Knowledge of fox vocalizations can be a valuable asset in wildlife conservation efforts.
- Population Monitoring: By recording and analyzing fox sounds, conservationists can monitor fox populations and track their distribution over time. This information can be used to assess the health of fox populations and to identify areas where conservation efforts are needed.
- Habitat Assessment: Fox sounds can be used to assess the quality of fox habitats. By comparing the sounds of foxes living in different areas, conservationists can determine which habitats are most suitable for them and which habitats are in need of restoration.
- Conflict Mitigation: Understanding fox sounds can help to mitigate human-wildlife conflicts. By identifying the sounds that foxes make when they are feeling threatened or stressed, conservationists can develop strategies to reduce human disturbance and to prevent conflicts from escalating.
By incorporating knowledge of fox sounds into conservation strategies, we can increase our chances of protecting these animals and their habitats for future generations. streetsounds.net contributes to wildlife conservation by raising awareness about urban wildlife and providing resources for responsible sound recording and analysis.
17. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Fox Sounds?
Common misconceptions about fox sounds include thinking all fox vocalizations are aggressive or that they sound like domestic dogs; in reality, fox sounds are diverse and have unique characteristics.
Several misconceptions exist regarding fox sounds, often stemming from a lack of familiarity with these animals and their behaviors.
- All Fox Sounds Are Aggressive: Many people assume that all fox vocalizations are aggressive or threatening. In reality, foxes produce a wide range of sounds, many of which are used for communication, courtship, and social bonding.
- Foxes Sound Like Domestic Dogs: While some fox vocalizations may resemble those of domestic dogs, their overall repertoire is distinct and reflects their specific communication needs and social behaviors.
- Foxes Only Vocalize at Night: Foxes are most active at dawn and dusk, but they can vocalize at any time of day, depending on the situation.
- Fox Sounds Are Always Loud: While some fox vocalizations can be quite loud (such as their screams), others are much more subtle and difficult to hear.
By dispelling these misconceptions, we can gain a more accurate understanding of fox behavior and communication. streetsounds.net addresses common misconceptions about urban soundscapes by providing accurate information and educational resources.
18. How Can I Learn More About Fox Sounds?
To learn more about fox sounds, explore online resources like streetsounds.net, listen to recordings of fox vocalizations, and consult with wildlife experts or local wildlife organizations.
Many resources are available for those interested in learning more about fox sounds.
- Online Resources: Websites like streetsounds.net offer information about fox vocalizations, as well as recordings and videos that can help you learn to identify different sounds.
- Recordings: Listening to recordings of fox vocalizations is a great way to familiarize yourself with their sounds. Many online resources offer free recordings of fox sounds, or you can purchase recordings from nature sound libraries.
- Wildlife Experts: Contacting wildlife experts or local wildlife organizations can provide valuable insights into fox behavior and communication. These experts may be able to offer guided tours, workshops, or other educational opportunities.
By taking advantage of these resources, you can deepen your knowledge of fox sounds and gain a greater appreciation for these fascinating animals. streetsounds.net serves as a central hub for urban sound enthusiasts, offering a wealth of information and resources for exploring the sounds of the city.
19. Are Fox Sounds Protected by Law?
Foxes themselves are protected by varying laws depending on the region; however, their sounds are generally not subject to specific legal protections unless they are recorded and used commercially without permission.
The legal protection of fox sounds is a complex issue that depends on a variety of factors.
- Protection of Foxes: In many countries, foxes are protected by laws that regulate hunting, trapping, and other forms of exploitation. These laws are designed to protect fox populations and to ensure their long-term survival.
- Copyright Law: If you record fox sounds, you may be able to obtain copyright protection for your recordings. This would give you the exclusive right to reproduce, distribute, and display your recordings.
- Commercial Use: If you plan to use fox sounds for commercial purposes (such as in a film, video game, or musical composition), you may need to obtain permission from the copyright holder of the recordings.
- Ethical Considerations: Regardless of the legal protections that may apply, it’s important to consider the ethical implications of recording and using fox sounds. Avoid disturbing foxes or disrupting their natural behaviors when recording their sounds.
By understanding the legal and ethical considerations surrounding fox sounds, you can ensure that you are using these sounds responsibly and ethically. streetsounds.net promotes responsible sound practices, encouraging users to respect wildlife and the environment when recording urban soundscapes.
20. How Do Fox Sounds Reflect Their Adaptation to Urban Environments?
In urban areas, foxes may alter their vocalizations to communicate more effectively amidst city noise or to signal their presence in fragmented habitats.
Foxes living in urban environments have had to adapt to a variety of challenges, including increased noise levels, fragmented habitats, and frequent encounters with humans. These challenges have led to changes in their behavior, including their vocalizations.
- Altered Vocalizations: Urban foxes may alter their vocalizations to communicate more effectively amidst city noise. For example, they may use louder or higher-frequency calls that can be heard above the din of traffic and construction.
- Signaling Presence: Urban foxes may use vocalizations to signal their presence in fragmented habitats. By calling out in these areas, they can let other foxes know that the territory is occupied and to avoid potential conflicts.
- Human Interaction: Urban foxes may use vocalizations to communicate with humans. For example, they may bark at humans who approach them, either to warn them to stay away or to beg for food.
By studying the sounds of urban foxes, we can gain a better understanding of how these animals are adapting to the challenges of living in a human-dominated landscape. streetsounds.net documents the unique soundscapes of urban environments, showcasing how wildlife adapts to city life.
Unlock the Symphony of the Streets with streetsounds.net
Ready to immerse yourself in the captivating world of urban sound? streetsounds.net invites you to explore our extensive library of high-quality sound effects, field recordings, and exclusive content. Whether you’re a filmmaker, musician, game developer, or simply a sound enthusiast, our platform offers the perfect sonic palette to bring your creative visions to life.
Here’s how streetsounds.net can elevate your projects:
- Unrivaled Sound Library: Discover a vast collection of meticulously recorded urban soundscapes, from bustling city streets to serene park ambiences.
- Exclusive Content: Access unique sound effects and recordings not found anywhere else, curated by our team of experienced sound professionals.
- Inspiring Articles & Interviews: Delve into the world of sound with our insightful articles, interviews with industry experts, and behind-the-scenes stories.
- Thriving Community: Connect with fellow sound enthusiasts, share your work, and collaborate on exciting projects in our vibrant online community.
Don’t miss out on the opportunity to:
- Enhance your films and videos with authentic urban soundscapes.
- Create immersive and engaging sound designs for your video games.
- Add unique sonic textures to your music productions.
- Simply explore the fascinating world of sound and discover new sonic possibilities.
Visit streetsounds.net today and start your sonic adventure!
Contact Us:
Address: 726 Broadway, New York, NY 10003, United States
Phone: +1 (212) 998-8550
Website: streetsounds.net
FAQ About Red Fox Sounds
1. What is the most common sound a red fox makes?
The most commonly heard sound is either the sharp ‘yapping’ bark (called a Staccato bark) that seems to be used by members of the group to maintain long-distance contact, or the wow-wow-wow bark, which appears to be a declaration of territory ownership.
2. Do red foxes sound like dogs?
While some fox vocalizations may resemble those of domestic dogs, their overall repertoire is distinct and reflects their specific communication needs and social behaviors.
3. What does it mean when a fox screams?
Vixens (female foxes) often use piercing screams to attract potential mates. These screams can carry over long distances and serve as an advertisement of their presence and readiness to mate.
4. Are red foxes loud animals?
Yes, some fox vocalizations can be quite loud (such as their screams), others are much more subtle and difficult to hear.
5. What time of year are foxes most vocal?
Foxes may call at any time of year, although they are most vocal during the breeding season (in my experience, particularly towards the end of winter).
6. Do male and female red foxes sound different?
Sexing individuals based on their contact calls may be more complicated because both sexes can make the various calls. That said, vixens often appear to terminate their ‘wow-wow-wow’ bark with a trailing ‘woooow’ (e.g., ‘wow-wow-wow-wow-woooow’), while dog foxes end theirs more abruptly.
7. What do baby red fox cubs sound like?
Baby foxes, also known as cubs, produce a variety of high-pitched vocalizations such as whelping calls, yelps, and warbles to communicate with their mother and siblings.
8. Do foxes communicate with each other silently?
Yes, foxes communicate using a combination of scent markings, body language, and a diverse range of vocalizations, each serving different purposes in their social interactions.
9. Can foxes purr like cats?
Similar to cats, foxes may produce a low, rumbling sound similar to a purr when feeling content or relaxed. This sound is often associated with close physical contact, such as cuddling with other foxes or being petted by a human.
10. How can I tell if a fox sound is a warning?
When angry or threatened, foxes typically emit growls, snarls, hisses, and aggressive barks, often accompanied by defensive body language such as flattened ears and raised fur.