Does bi-amping sound better? Absolutely, bi-amping can significantly enhance your audio experience by separating high and low frequencies, leading to cleaner, more detailed sound, and at streetsounds.net, we’re dedicated to helping you unlock the full potential of your audio system. By exploring the world of bi-amping and understanding its benefits, you can elevate your listening experience to new heights, enjoying enhanced clarity and depth in your favorite music, film scores, and street soundscapes. Discover the improvement in sonic fidelity, amplified sonic detail, and speaker wire.
1. What is Bi-amping and How Does it Work?
Bi-amping involves using two separate amplifiers to power the high-frequency (tweeter) and low-frequency (woofer) sections of a speaker; this helps in refining sound quality. This configuration minimizes intermodulation distortion and improves overall clarity.
1.1. Understanding the Basics of Bi-amping
Bi-amping isn’t just a fancy term; it’s a technique that audiophiles and music enthusiasts use to get the best possible sound from their speakers. Instead of using a single amplifier to power the entire speaker, bi-amping splits the job into two. One amplifier powers the high-frequency driver (tweeter), responsible for the crisp, clear treble sounds. The other amplifier powers the low-frequency driver (woofer), which delivers the deep, rich bass tones. Think of it like having two specialized chefs in a kitchen, each focused on perfecting their dish, rather than one chef trying to do everything at once.
1.2. Active vs. Passive Bi-amping: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to bi-amping, there are two main approaches: active and passive. Passive bi-amping is the simpler of the two. It uses the speaker’s existing passive crossover network, which is a set of components inside the speaker that divides the audio signal into high and low frequencies. You simply remove the jumper wires or bridging bars on the back of your speakers (if they have them) and connect separate amplifier channels to the high and low frequency terminals.
Active bi-amping, on the other hand, is a more advanced technique. It involves removing the passive crossover network from the speaker and using an external active crossover. An active crossover is an electronic device that splits the audio signal before it reaches the amplifiers. This allows for more precise control over the crossover frequencies and slopes, and it can result in even better sound quality. However, active bi-amping requires more technical knowledge and equipment.
1.3. The Role of Crossovers in Bi-amping
Crossovers are essential components in any bi-amping setup, whether active or passive. They act as traffic controllers, directing the right frequencies to the right drivers. In passive bi-amping, the speaker’s built-in crossover network does this job. It filters out the low frequencies from the signal sent to the tweeter and the high frequencies from the signal sent to the woofer.
In active bi-amping, the external active crossover performs this function. Because it operates at line level (before the amplification stage), it can use more sophisticated filtering techniques and provide more precise control over the frequencies sent to each driver. This can result in a smoother, more accurate sound.
1.4. Exploring the Benefits of Bi-amping: A Detailed Look
Bi-amping offers several potential benefits, which is why it’s a popular technique among audiophiles and sound enthusiasts:
- Reduced Intermodulation Distortion: This is arguably the most significant benefit. When a single amplifier powers both the woofer and tweeter, the large current demands of the woofer can modulate the signal going to the tweeter, creating distortion. By using separate amplifiers, this interaction is minimized, resulting in cleaner, more transparent sound.
- Increased Headroom: Each amplifier only has to handle a portion of the frequency spectrum, so they have more power available to reproduce those frequencies accurately. This can lead to greater dynamic range and the ability to play louder without distortion.
- Improved Driver Control: With a dedicated amplifier for each driver, the amplifier has better control over the movement of the woofer and tweeter. This can result in tighter, more accurate bass and more precise imaging.
- Flexibility: Bi-amping allows you to experiment with different amplifiers for the high and low frequencies, tailoring the sound to your preferences. For example, you might use a tube amplifier for the tweeters to get a warmer sound and a solid-state amplifier for the woofers to get more punch.
2. Why Does Bi-amping Potentially Sound Better?
Bi-amping can lead to noticeable improvements in sound quality because it reduces intermodulation distortion, provides increased headroom, and offers better control over the speakers. It refines musical nuances.
2.1. The Science Behind Improved Sound Quality with Bi-amping
The perceived improvement in sound quality with bi-amping can be attributed to several factors rooted in the physics of audio reproduction:
- Reduced Intermodulation Distortion (IMD): IMD occurs when two or more frequencies are processed simultaneously through a non-linear device, such as an amplifier. The result is the creation of new frequencies that are not present in the original signal, leading to a muddy or harsh sound. In a single-amplifier setup, the high-current demands of the woofer can affect the amplifier’s ability to accurately reproduce the delicate high-frequency signals sent to the tweeter. Bi-amping minimizes this interaction by providing separate amplifiers for each frequency range, reducing IMD.
- Decreased Distortion: According to research from the Audio Engineering Society, bi-amping reduces distortion and enhances sound clarity. By using separate amplifiers, each speaker receives a cleaner signal, leading to a more accurate sound.
- Enhanced Dynamic Range: Dynamic range refers to the difference between the quietest and loudest sounds a system can reproduce. Bi-amping can increase dynamic range by providing each driver with its own dedicated power source. This allows the system to reproduce both subtle nuances and powerful crescendos with greater accuracy and clarity.
- Improved Transient Response: Transient response refers to a system’s ability to accurately reproduce sudden changes in the audio signal, such as the attack of a drumbeat or the pluck of a guitar string. Bi-amping can improve transient response by providing each driver with better control over its movement. This results in a more precise and detailed sound.
2.2. Minimizing Intermodulation Distortion for Cleaner Audio
Intermodulation distortion (IMD) is a significant concern in audio systems, and bi-amping offers a way to minimize its effects. IMD occurs when different frequencies interact within the amplifier, creating unwanted artifacts in the sound. This is particularly problematic when a single amplifier is used to power both the high-frequency (tweeter) and low-frequency (woofer) sections of a speaker.
By separating the amplification duties, bi-amping reduces the likelihood of IMD. Each amplifier is dedicated to a specific frequency range, allowing it to operate more efficiently and accurately. This results in a cleaner, more transparent sound with improved clarity and detail.
2.3. Enhancing Headroom and Dynamic Range with Bi-amping
Headroom refers to the amount of extra power an amplifier has available beyond its normal operating level. Having ample headroom is important because it allows the amplifier to handle sudden peaks in the audio signal without clipping or distorting.
Bi-amping can enhance headroom by providing each driver with its own dedicated amplifier. This means that each amplifier only has to handle a portion of the frequency spectrum, allowing it to operate more efficiently and with greater reserve power. The result is an increased dynamic range, which refers to the difference between the quietest and loudest sounds a system can reproduce.
2.4. The Impact of Bi-amping on Transient Response and Imaging
Transient response refers to a speaker’s ability to accurately reproduce sudden changes in the audio signal, such as the sharp attack of a drumbeat or the pluck of a guitar string. A good transient response is essential for creating a realistic and engaging listening experience.
Bi-amping can improve transient response by providing each driver with better control over its movement. With a dedicated amplifier for each driver, the amplifier can respond more quickly and accurately to changes in the audio signal.
Imaging refers to the ability of a sound system to create a realistic and three-dimensional soundstage. A good imaging system will allow you to pinpoint the location of each instrument or sound within the music.
Bi-amping can improve imaging by reducing intermodulation distortion and providing better driver control. This results in a more precise and stable soundstage, with improved separation and localization of instruments.
3. Setting Up Your Bi-amped System
Setting up a bi-amped system requires careful attention to detail, including removing jumper cables, configuring the receiver, and connecting the speaker wires correctly. Pay close attention to terminal connections.
3.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Bi-amping Your Speakers
Bi-amping your speakers can seem daunting, but with a step-by-step approach, it can be a straightforward process. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
- Check Compatibility: Ensure your speakers and AV receiver support bi-amping. Look for two sets of terminals on the back of your speakers and a bi-amp setting in your receiver’s manual.
- Power Down: Turn off your AV receiver and speakers before making any connections. This prevents damage to your equipment.
- Remove Jumper Cables: On the back of your speakers, you’ll find jumper cables or bridging bars connecting the high-frequency and low-frequency terminals. Remove these carefully.
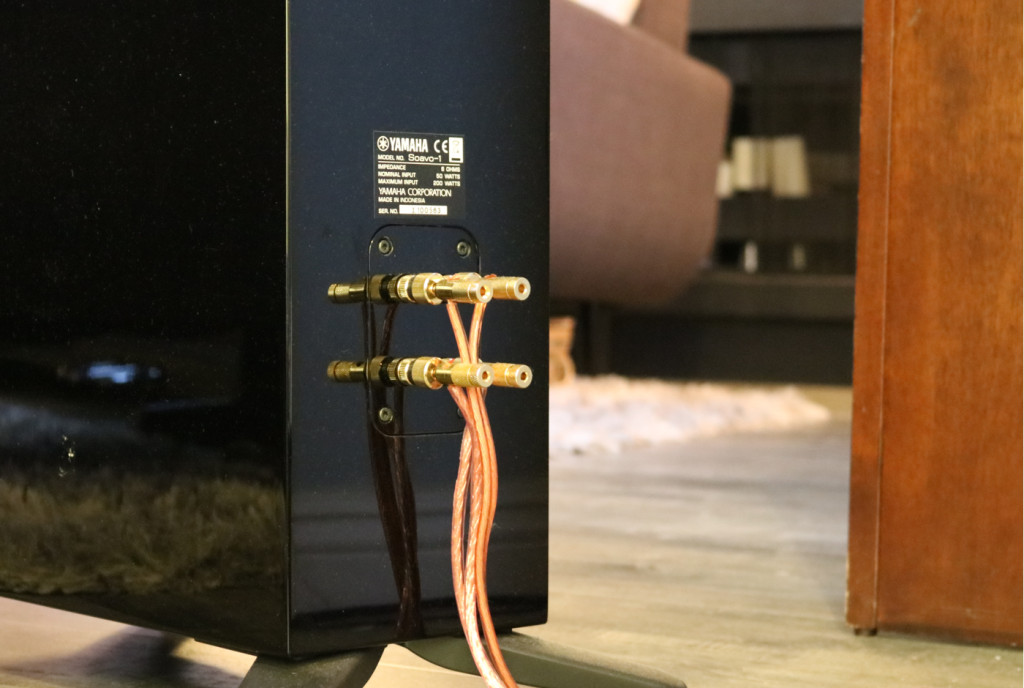 Close-up of the back of a speaker where wires attach.
Close-up of the back of a speaker where wires attach.
Any speaker with two sets of terminals can be bi-amped. - Configure Your Receiver: Access your receiver’s menu system and locate the bi-amp setting. Enable this setting to route the appropriate amplifier channels to the bi-amp terminals.
- Connect Speaker Wires: Connect one pair of speaker wires from the bi-amp terminals on your receiver to one set of inputs on the back of your speaker. Pay close attention to the polarity, ensuring that the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals are connected correctly.
- Connect Main Speaker Output: Connect the receiver’s Main (front) Left speaker output to the second set of connections on the left speaker. Again, ensure correct polarity.
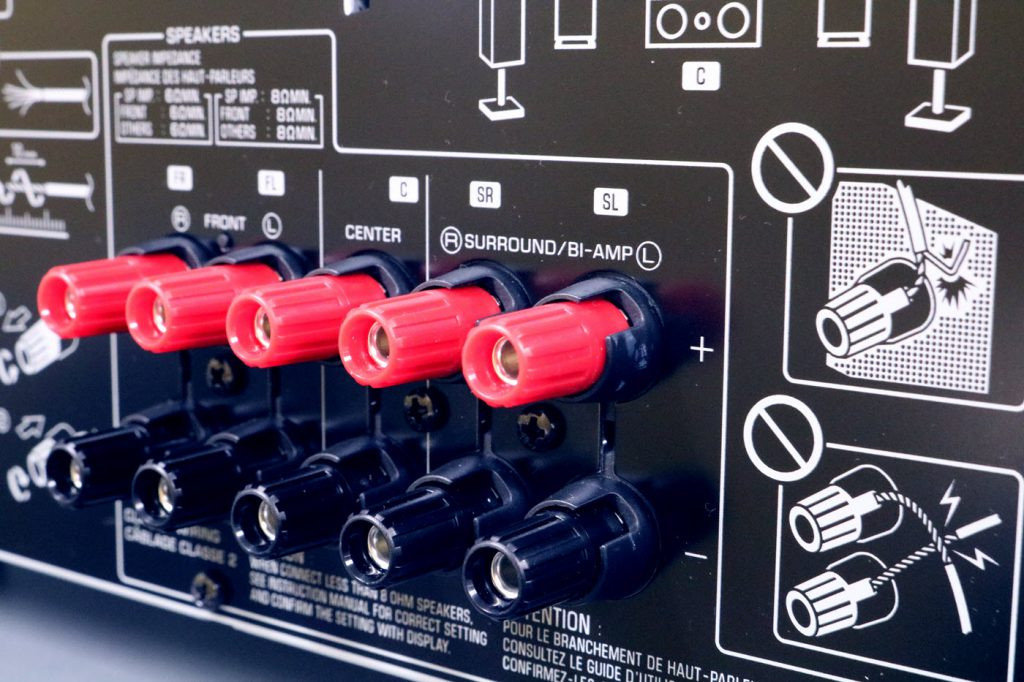 Closeup of terminals on back of receiver.
Closeup of terminals on back of receiver.
The speaker terminals on the right can be used for bi-amping. - Repeat for Right Speaker: Repeat steps 5 and 6 for the right speaker, ensuring all connections are secure and correct.
- Double-Check Connections: Before powering on your system, double-check all connections to ensure they are secure and that the polarity is correct.
- Power On and Enjoy: Power on your AV receiver and speakers and enjoy the enhanced sound quality of your bi-amped system.
3.2. Choosing the Right Amplifiers for Bi-amping
Selecting the right amplifiers is crucial for optimizing your bi-amping setup. Here are some factors to consider:
- Power Rating: Ensure that the amplifiers have sufficient power to drive your speakers. Match the amplifier’s power rating to the speakers’ power handling capabilities.
- Amplifier Type: Consider using different amplifier types for the high-frequency and low-frequency sections. For example, a tube amplifier for the tweeters can provide a warmer, more detailed sound, while a solid-state amplifier for the woofers can deliver more punch and control.
- Impedance Matching: Match the amplifier’s output impedance to the speaker’s impedance. This ensures optimal power transfer and prevents damage to your equipment.
- Sound Quality: Listen to different amplifiers and choose the ones that sound best to your ears. Consider factors such as clarity, detail, and overall tonal balance.
3.3. Speaker Wire Selection: Does it Really Matter?
The choice of speaker wire can have a subtle but noticeable impact on sound quality. While some audiophiles argue that expensive speaker cables are essential, others believe that standard gauge wire is sufficient. Here are some factors to consider:
- Gauge: The gauge of the speaker wire refers to its thickness. Thicker wires (lower gauge numbers) have less resistance and can carry more current. For bi-amping, it’s generally recommended to use 16-gauge or 14-gauge wire.
- Material: Speaker wires are typically made of copper or silver. Copper is a good conductor and is relatively inexpensive. Silver is a better conductor but is more expensive.
- Construction: Speaker wires come in various constructions, such as stranded or solid-core. Stranded wires are more flexible and easier to work with, while solid-core wires are said to provide better sound quality.
- Length: Keep the speaker wires as short as possible to minimize resistance. If you need to run long lengths of wire, use a thicker gauge to compensate for the increased resistance.
3.4. Optimizing Your Bi-amping Setup for the Best Sound
Once you’ve set up your bi-amped system, there are several things you can do to optimize it for the best possible sound:
- Experiment with Amplifier Placement: Try different positions for your amplifiers to minimize interference and improve soundstaging.
- Adjust Crossover Frequencies: If you’re using an active crossover, experiment with different crossover frequencies to find the setting that sounds best to your ears.
- Fine-Tune Amplifier Gain: Adjust the gain on each amplifier to balance the levels of the high-frequency and low-frequency sections.
- Listen Critically: Listen to a variety of music and pay attention to the clarity, detail, and overall tonal balance of your system. Make adjustments as needed to achieve the sound you desire.
4. Bi-wiring vs. Bi-amping: What’s the Difference?
Bi-wiring involves using separate speaker cables for the high and low-frequency signals but still uses a single amplifier; this differs from bi-amping, which uses separate amplifiers. Bi-amping provides more potential benefits.
4.1. Understanding Bi-wiring: An Alternative Approach
Bi-wiring is often confused with bi-amping, but they are distinct techniques. Bi-wiring involves using separate speaker cables to connect the amplifier to the high-frequency and low-frequency terminals on the speaker. However, unlike bi-amping, bi-wiring still uses a single amplifier to power both frequency ranges.
The idea behind bi-wiring is that it reduces interaction between the high-frequency and low-frequency signals in the speaker cable. By using separate cables, the high-frequency signals are less likely to be affected by the large current demands of the woofer, resulting in cleaner sound.
4.2. The Key Differences Between Bi-amping and Bi-wiring
The key difference between bi-amping and bi-wiring lies in the number of amplifiers used. Bi-amping uses separate amplifiers for the high-frequency and low-frequency sections, while bi-wiring uses a single amplifier with separate speaker cables.
This difference has several implications for sound quality. Bi-amping provides more potential benefits because it reduces intermodulation distortion, increases headroom, and offers better driver control. Bi-wiring, on the other hand, primarily focuses on reducing interaction between the high-frequency and low-frequency signals in the speaker cable.
4.3. When to Choose Bi-amping Over Bi-wiring (and Vice Versa)
The choice between bi-amping and bi-wiring depends on your budget, equipment, and desired level of sound quality.
- Choose Bi-amping if:
- You want the best possible sound quality.
- You have a receiver or amplifier with spare channels that can be used for bi-amping.
- You’re willing to invest in an additional amplifier.
- Choose Bi-wiring if:
- You want a simple and relatively inexpensive way to improve sound quality.
- You don’t have spare amplifier channels or the budget for an additional amplifier.
- You’re primarily concerned about reducing interaction between the high-frequency and low-frequency signals in the speaker cable.
4.4. Debunking Myths About Bi-wiring and Bi-amping
There are many myths and misconceptions surrounding bi-wiring and bi-amping. Here are some of the most common ones, debunked:
- Myth: Bi-wiring and bi-amping will make your speakers sound twice as loud.
- Reality: While bi-amping can increase headroom and dynamic range, it won’t significantly increase the overall loudness of your speakers.
- Myth: You need expensive speaker cables for bi-wiring and bi-amping to make a difference.
- Reality: While high-quality speaker cables can potentially improve sound quality, they are not essential for bi-wiring or bi-amping to make a noticeable difference.
- Myth: Bi-wiring and bi-amping are only for audiophiles with high-end equipment.
- Reality: Bi-wiring and bi-amping can benefit anyone who wants to improve the sound quality of their system, regardless of the equipment’s price or sophistication.
5. Common Misconceptions About Bi-amping
There are several misconceptions about bi-amping, including its impact on loudness and the necessity of expensive cables. Understanding these can help you make informed decisions.
5.1. Does Bi-amping Make My Speakers Louder?
One common misconception about bi-amping is that it will make your speakers significantly louder. While bi-amping can increase headroom and dynamic range, it won’t drastically increase the overall loudness of your system.
Loudness is primarily determined by the amplifier’s power output and the speaker’s sensitivity. Bi-amping doesn’t change either of these factors. Instead, it improves the efficiency and accuracy of the amplifier, resulting in cleaner, more detailed sound.
5.2. Do I Need Expensive Cables for Bi-amping to Work?
Another misconception is that you need to invest in expensive speaker cables for bi-amping to make a difference. While high-quality speaker cables can potentially improve sound quality, they are not essential for bi-amping to provide noticeable benefits.
The primary advantage of bi-amping is that it reduces intermodulation distortion and improves driver control. These benefits are largely independent of the quality of the speaker cables used.
5.3. Is Bi-amping Only for High-End Audio Systems?
Bi-amping is often associated with high-end audio systems, but it can benefit anyone who wants to improve the sound quality of their system, regardless of the equipment’s price or sophistication.
Even with modest equipment, bi-amping can result in noticeable improvements in clarity, detail, and overall tonal balance. The key is to ensure that your speakers and receiver support bi-amping and that you follow the setup instructions carefully.
5.4. Can Bi-amping Damage My Speakers?
When done correctly, bi-amping will not damage your speakers. However, it’s essential to follow the setup instructions carefully and to ensure that the amplifiers are properly matched to the speakers.
One potential risk is overpowering the speakers. If you use excessively powerful amplifiers, you could damage the drivers. It’s also important to ensure that the polarity of the speaker wires is correct, as incorrect polarity can cause distortion and potentially damage the speakers.
6. Real-World Examples of Bi-amping in Action
Many professional audio engineers and home theater enthusiasts use bi-amping to achieve superior sound quality. Understanding how they apply bi-amping can offer practical insights.
6.1. Bi-amping in Professional Recording Studios
In professional recording studios, bi-amping is often used to power studio monitors, which are high-quality speakers used for mixing and mastering music. Bi-amping allows engineers to hear the music with greater clarity and detail, making it easier to make critical decisions about the mix.
For example, a recording studio might use a high-powered solid-state amplifier to drive the woofers in their studio monitors, providing the necessary punch and control for accurate bass reproduction. They might then use a tube amplifier to drive the tweeters, providing a smoother, more detailed sound for the high frequencies.
6.2. Bi-amping in Home Theater Systems
Bi-amping is also popular in home theater systems, where it can enhance the movie-watching experience by providing clearer dialogue, more impactful sound effects, and a more immersive soundstage.
Many home theater enthusiasts choose to bi-amp their front speakers, which are responsible for the majority of the sound in a movie. By bi-amping these speakers, they can create a more realistic and engaging listening experience.
6.3. Bi-amping in Live Sound Reinforcement
In live sound reinforcement, bi-amping is used to power the speakers used at concerts and other live events. Bi-amping allows sound engineers to have more control over the sound and to ensure that the music is reproduced accurately and powerfully.
For example, a sound engineer might use a separate amplifier for each driver in a multi-way speaker system, allowing them to fine-tune the sound and optimize it for the venue.
6.4. Case Studies: Successful Bi-amping Implementations
There are many case studies of successful bi-amping implementations, demonstrating the benefits of this technique.
- Case Study 1: A home theater enthusiast bi-amped their front speakers using a pair of high-quality amplifiers. The result was a noticeable improvement in clarity, detail, and soundstaging, making their movie-watching experience more immersive.
- Case Study 2: A recording studio bi-amped their studio monitors using a combination of solid-state and tube amplifiers. The result was a more accurate and detailed sound, allowing them to make better mixing decisions.
- Case Study 3: A live sound engineer bi-amped the speakers used at a concert, resulting in a more powerful and controlled sound that filled the venue.
7. Exploring Streetsounds.net: Your Resource for Audio Enhancement
streetsounds.net offers a wealth of resources for enhancing your audio experience, including a diverse sound library and expert articles. Dive into our content to elevate your sound quality.
7.1. Discovering Unique Sound Effects on Streetsounds.net
At streetsounds.net, we pride ourselves on providing a unique and diverse collection of sound effects. Whether you’re a music producer, filmmaker, or game designer, you’ll find the perfect sounds to bring your projects to life.
Our sound library includes a wide range of urban soundscapes, from the bustling streets of New York City to the quiet alleys of small towns. We also offer a variety of sound effects, such as car horns, sirens, construction noises, and crowd sounds.
7.2. Expert Articles and Guides on Audio Optimization
In addition to our sound library, streetsounds.net also offers a wealth of expert articles and guides on audio optimization. Whether you’re looking to improve the sound quality of your home theater system, your recording studio, or your live sound setup, you’ll find valuable information and tips on our website.
Our articles cover a wide range of topics, including bi-amping, equalization, compression, and microphone techniques. We also offer guides on choosing the right equipment for your needs and setting up your system for optimal performance.
7.3. Connecting with the Streetsounds.net Community
streetsounds.net is more than just a website; it’s a community of audio enthusiasts, music producers, filmmakers, and game designers. Our online forum is a great place to connect with other like-minded individuals, share your experiences, and ask questions.
We also host regular online events, such as webinars and Q&A sessions with industry experts. These events are a great way to learn new skills, network with other professionals, and stay up-to-date on the latest trends in the audio industry.
7.4. How Streetsounds.net Can Help You Achieve Better Sound
Whether you’re a seasoned audio professional or just starting out, streetsounds.net can help you achieve better sound. Our unique sound library, expert articles, and vibrant community provide everything you need to take your audio projects to the next level.
Explore our website today and discover the difference that streetsounds.net can make. Address: 726 Broadway, New York, NY 10003, United States. Phone: +1 (212) 998-8550.
8. The Future of Audio: Trends and Innovations
The audio industry is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. Staying informed about these developments can help you optimize your audio setup.
8.1. Emerging Trends in Speaker Technology
Speaker technology is constantly evolving, with new materials, designs, and techniques being developed all the time. Some of the most exciting trends in speaker technology include:
- Wireless Speakers: Wireless speakers are becoming increasingly popular, offering convenience and flexibility. Many wireless speakers use Bluetooth or Wi-Fi to connect to your audio source, eliminating the need for cables.
- Smart Speakers: Smart speakers combine wireless technology with voice assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant. This allows you to control your music and other smart home devices with your voice.
- Immersive Audio: Immersive audio technologies like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X are creating more realistic and engaging listening experiences. These technologies use multiple speakers to create a three-dimensional soundstage.
- Miniaturization: Speaker technology is becoming increasingly miniaturized, allowing for smaller and more portable speakers without sacrificing sound quality.
8.2. Innovations in Amplifier Design
Amplifier design is also constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques being developed to improve efficiency, reduce distortion, and enhance sound quality. Some of the most exciting innovations in amplifier design include:
- Class D Amplifiers: Class D amplifiers are highly efficient, converting a large percentage of the power they consume into audio output. This makes them ideal for portable devices and energy-efficient systems.
- Digital Amplifiers: Digital amplifiers use digital signal processing (DSP) to improve sound quality and provide greater control over the audio signal.
- Hybrid Amplifiers: Hybrid amplifiers combine the best features of tube and solid-state amplifiers, providing a warm, detailed sound with the power and efficiency of solid-state technology.
8.3. The Role of Digital Signal Processing (DSP) in Audio Enhancement
Digital signal processing (DSP) plays an increasingly important role in audio enhancement. DSP is used to manipulate the audio signal in various ways, such as equalization, compression, and noise reduction.
DSP can be used to improve the sound quality of your audio system, correct for imperfections in your listening environment, and create custom sound profiles. Many modern receivers and amplifiers include built-in DSP capabilities, allowing you to fine-tune the sound to your preferences.
8.4. Predictions for the Future of Audio
The future of audio is likely to be shaped by several key trends, including:
- Increased Use of Wireless Technology: Wireless technology will continue to become more prevalent in audio systems, offering greater convenience and flexibility.
- Greater Integration of AI and Voice Control: AI and voice control will become increasingly integrated into audio systems, allowing you to control your music and other devices with your voice.
- More Immersive and Personalized Listening Experiences: Immersive audio technologies and personalized sound profiles will create more realistic and engaging listening experiences.
- Continued Miniaturization and Portability: Speaker and amplifier technology will continue to become more miniaturized and portable, allowing you to enjoy high-quality audio on the go.
9. FAQ: Answering Your Questions About Bi-amping
Addressing common questions about bi-amping can help clarify its benefits and practical applications. Here are some frequently asked questions to guide you.
9.1. Can I Bi-amp With Any Speakers?
No, not all speakers are designed for bi-amping. To bi-amp, your speakers must have two sets of terminals on the back, one for the high-frequency driver (tweeter) and one for the low-frequency driver (woofer). If your speakers only have one set of terminals, they cannot be bi-amped.
9.2. Will Bi-amping Damage My Speakers?
No, bi-amping will not damage your speakers if done correctly. However, it’s important to follow the setup instructions carefully and to ensure that the amplifiers are properly matched to the speakers. Overpowering the speakers with excessively powerful amplifiers can damage the drivers.
9.3. What Kind of Amplifier Do I Need for Bi-amping?
For bi-amping, you need two separate amplifiers, one for the high-frequency section and one for the low-frequency section. The amplifiers should be matched to the speakers in terms of power rating and impedance. You can use two identical amplifiers or experiment with different amplifier types for the high and low frequencies.
9.4. Does Bi-amping Require an Active Crossover?
No, bi-amping does not necessarily require an active crossover. You can bi-amp using the speaker’s existing passive crossover network (passive bi-amping) or remove the passive crossover and use an external active crossover (active bi-amping). Active bi-amping provides more precise control over the crossover frequencies and slopes but requires more technical knowledge and equipment.
9.5. Is Bi-amping Worth the Effort and Expense?
Whether bi-amping is worth the effort and expense depends on your budget, equipment, and desired level of sound quality. Bi-amping can provide noticeable improvements in clarity, detail, and soundstaging, but it requires an additional amplifier and careful setup. If you’re serious about audio quality, bi-amping is worth considering.
9.6. Can I Use a Stereo Amplifier for Bi-amping?
Yes, you can use a stereo amplifier for bi-amping if it has four channels. Each channel can be connected to a separate driver in the speaker.
9.7. What Are the Benefits of Active Bi-amping Over Passive Bi-amping?
Active bi-amping offers several potential benefits over passive bi-amping:
- More Precise Control: Active crossovers allow for more precise control over the crossover frequencies and slopes.
- Lower Distortion: Active crossovers operate at line level, before the amplification stage, which can result in lower distortion.
- Greater Flexibility: Active bi-amping allows you to experiment with different crossover settings and amplifier combinations to fine-tune the sound to your preferences.
9.8. How Do I Choose the Right Crossover Frequency for Active Bi-amping?
The ideal crossover frequency for active bi-amping depends on the specific speakers you are using and your listening preferences. A good starting point is to use the speaker manufacturer’s recommended crossover frequency. You can then experiment with different frequencies to find the setting that sounds best to your ears.
9.9. Will Bi-amping Fix Problems With My Speakers?
Bi-amping can improve the sound quality of your speakers, but it won’t fix underlying problems such as damaged drivers or faulty crossover components. If your speakers have problems, you should address those issues first before considering bi-amping.
9.10. Can Bi-amping Improve the Sound of Older Speakers?
Yes, bi-amping can often improve the sound of older speakers by reducing intermodulation distortion and providing better driver control. This can result in a cleaner, more detailed sound, even with older equipment.
10. Taking the Next Step: Enhancing Your Audio Experience
Ready to elevate your audio experience? Explore the resources and community at streetsounds.net to discover new sounds and techniques for audio enhancement.
10.1. Exploring Advanced Audio Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics of bi-amping, there are many other advanced audio techniques you can explore to further enhance your listening experience. Some of these techniques include:
- Equalization: Equalization (EQ) involves adjusting the frequency response of your audio system to correct for imperfections in your listening environment and to fine-tune the sound to your preferences.
- Compression: Compression is used to reduce the dynamic range of an audio signal, making it sound louder and more consistent. Compression can be useful for improving the clarity of vocals and for adding punch to drums.
- Reverb: Reverb is used to simulate the sound of a physical space, adding depth and ambience to your recordings.
- Delay: Delay is used to create echoes and other time-based effects.
10.2. Joining the Streetsounds.net Community for Support and Inspiration
The streetsounds.net community is a great place to connect with other audio enthusiasts, share your experiences, and get support and inspiration. Our online forum is a welcoming and informative space where you can ask questions, share tips, and discuss the latest trends in audio technology.
We also host regular online events, such as webinars and Q&A sessions with industry experts. These events are a great way to learn new skills, network with other professionals, and stay up-to-date on the latest developments in the audio industry.
10.3. Stay Updated With streetsounds.net
Sign up for the streetsounds.net newsletter to receive updates on new sound effects, expert articles, and community events. Stay connected to the latest trends and techniques in the audio world.
10.4. Ready to Dive In? Visit streetsounds.net Today
Visit streetsounds.net today to explore our unique sound library, expert articles, and vibrant community. Discover the difference that streetsounds.net can make in your audio projects. Start exploring new sounds, learn from industry experts, and connect with a community of passionate audio enthusiasts. Your journey to exceptional sound starts here.

