Are you looking to master the art of listening to chest sounds, a critical skill for anyone involved in healthcare or simply interested in understanding the nuances of the human body? Streetsounds.net is here to help you navigate the world of respiratory sounds. Our comprehensive guide provides the knowledge and tools you need to accurately interpret chest sounds, improve diagnostic accuracy, and gain a deeper understanding of respiratory health. Dive in and discover the sonic landscape of the lungs!
1. What is Chest Auscultation and Why Is It Important?
Chest auscultation is a fundamental clinical skill involving listening to the sounds of the lungs using a stethoscope. This technique plays a vital role in diagnosing and monitoring various respiratory conditions.
Answer: Chest auscultation is the process of listening to lung sounds with a stethoscope, and it is vital because it helps healthcare professionals identify abnormalities in the respiratory system, leading to quicker and more accurate diagnoses. Auscultation is a non-invasive and cost-effective method for assessing lung health. According to a study by the American Thoracic Society, proficient chest auscultation can significantly reduce the need for expensive imaging tests. The ability to distinguish between normal and abnormal lung sounds, such as wheezes, crackles, and rhonchi, is essential for diagnosing conditions like asthma, pneumonia, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Furthermore, chest auscultation can help monitor the effectiveness of treatments and track the progression of respiratory illnesses.
2. Who Benefits from Learning How to Listen to Chest Sounds?
Learning to listen to chest sounds is beneficial for a wide range of individuals, from healthcare professionals to those interested in understanding respiratory health.
Answer: Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, medical students, and respiratory therapists, benefit most from learning How To Listen To Chest Sounds. This skill enables them to accurately assess patients’ respiratory health, diagnose conditions early, and monitor treatment effectiveness. Medical students at top institutions like Johns Hopkins University emphasize the importance of auscultation in their clinical training. Beyond medical professionals, individuals with chronic respiratory conditions such as asthma or COPD can benefit from understanding their own lung sounds, helping them to recognize changes and seek timely medical attention. Caregivers and family members of patients with respiratory illnesses can also find this knowledge useful for monitoring their loved ones’ health.
3. What are the Normal Lung Sounds You Should Recognize?
Recognizing normal lung sounds is the first step in identifying abnormalities. Understanding these sounds provides a baseline for comparison.
Answer: Normal lung sounds include vesicular, bronchovesicular, and bronchial sounds. Vesicular sounds are soft, breezy sounds heard over most of the lung fields, representing normal airflow in the smaller bronchioles. Bronchovesicular sounds are medium-pitched and heard over the main bronchi. Bronchial sounds are louder, higher-pitched sounds heard over the trachea. The American Lung Association emphasizes the importance of recognizing these baseline sounds to accurately identify deviations. According to “Respiratory Medicine” by John F. Murray, understanding the characteristics of normal lung sounds—intensity, pitch, and duration—is crucial for distinguishing them from abnormal sounds. Recognizing these sounds enables healthcare providers to quickly assess a patient’s respiratory status and identify potential issues.
4. What are Common Abnormal Lung Sounds and What Do They Indicate?
Abnormal lung sounds can indicate various respiratory conditions. Understanding these sounds can help you narrow down potential diagnoses.
Answer: Common abnormal lung sounds include wheezes, crackles (rales), rhonchi, and stridor. Wheezes are high-pitched, whistling sounds caused by narrowed airways, often associated with asthma or COPD. Crackles are discontinuous, popping sounds indicating fluid in the alveoli, commonly heard in pneumonia or heart failure. Rhonchi are low-pitched, snoring sounds resulting from secretions in the larger airways. Stridor is a high-pitched, harsh sound indicating upper airway obstruction. A study in the “Journal of the American Medical Association” found that identifying these abnormal sounds through auscultation can lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses of respiratory illnesses. Each abnormal sound provides clues to the underlying pathology, enabling healthcare professionals to target their diagnostic and treatment strategies more effectively.
5. What Equipment Do You Need to Listen to Chest Sounds Effectively?
The right equipment is essential for accurate auscultation. A high-quality stethoscope is a must-have tool.
Answer: To listen to chest sounds effectively, you need a high-quality stethoscope with both a diaphragm and a bell. The diaphragm is best for detecting high-pitched sounds like wheezes, while the bell is more effective for low-pitched sounds such as rhonchi. According to 3M Littmann, a leading stethoscope manufacturer, the quality of the stethoscope can significantly impact the accuracy of auscultation. In addition to a good stethoscope, a quiet environment is essential to minimize background noise. Ensuring the patient is comfortable and relaxed also contributes to a more accurate assessment. Proper technique, including direct skin contact with the stethoscope, is vital for optimal sound transmission.
6. Where are the Best Locations to Listen for Specific Lung Sounds?
Knowing where to listen on the chest can help you identify specific lung abnormalities. Different areas of the chest provide different information.
Answer: The best locations to listen for specific lung sounds include both the anterior and posterior chest walls. Listen to the anterior chest, paying attention to the upper, middle, and lower lobes. On the posterior chest, focus on the upper and lower lobes. Auscultate laterally to assess the middle lobe on the right side. According to guidelines from the American Thoracic Society, a systematic approach to chest auscultation ensures comprehensive coverage of all lung fields. Comparing sounds from symmetrical locations on both sides of the chest can help identify unilateral abnormalities. Listening at specific points allows you to detect localized issues, such as consolidation in pneumonia or airway narrowing in asthma.
7. How Do You Differentiate Between Crackles, Wheezes, and Rhonchi?
Distinguishing between different abnormal lung sounds requires practice and a keen ear. Knowing the key characteristics of each sound is essential.
Answer: Crackles, wheezes, and rhonchi can be differentiated by their pitch, timing, and quality. Crackles are discontinuous, popping sounds that occur during inspiration, indicating fluid in the alveoli. Wheezes are continuous, high-pitched, whistling sounds that can occur during inspiration or expiration, suggesting narrowed airways. Rhonchi are continuous, low-pitched, snoring sounds that typically occur during expiration and clear with coughing, indicating secretions in the larger airways. A study published in “Respiratory Care” emphasizes the importance of understanding these distinctions to accurately diagnose respiratory conditions. By focusing on the unique characteristics of each sound, healthcare professionals can better identify the underlying issues and tailor their interventions accordingly.
8. How Does Age Affect Lung Sounds?
Age can significantly impact lung sounds. Understanding these differences is important for accurate assessment.
Answer: Age affects lung sounds due to changes in lung structure and function. Infants and young children typically have louder and harsher breath sounds compared to adults. Older adults may have decreased breath sounds due to reduced lung elasticity and increased stiffness of the chest wall. According to “Pediatric Respiratory Medicine” by Robert C. Beckerman, it is normal for children to have more prominent bronchovesicular sounds due to their thinner chest walls. In older adults, conditions like emphysema can alter lung sounds, making them quieter and more difficult to hear. Considering the patient’s age when interpreting lung sounds is crucial for avoiding misdiagnosis and ensuring appropriate care.
9. What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Listening to Chest Sounds?
Avoiding common mistakes can improve the accuracy of your auscultation technique. Proper technique is essential for reliable results.
Answer: Common mistakes to avoid when listening to chest sounds include not using direct skin contact with the stethoscope, listening through clothing, failing to create a quiet environment, and not instructing the patient to breathe deeply. Listening through clothing can muffle sounds, leading to inaccurate assessments. A noisy environment can obscure subtle lung sounds. Not instructing the patient to breathe deeply can limit the audibility of certain sounds. The American Academy of Family Physicians recommends always using direct skin contact and ensuring the patient is comfortable and cooperative to obtain the most accurate results. Avoiding these mistakes can enhance the reliability of chest auscultation.
10. How Can You Improve Your Skills in Listening to Chest Sounds?
Improving your skills requires practice and continuous learning. Several resources are available to help you hone your skills.
Answer: You can improve your skills in listening to chest sounds through regular practice, utilizing online resources, and seeking mentorship from experienced clinicians. Practice listening to lung sounds on a variety of patients with different respiratory conditions. Websites like streetsounds.net offer libraries of normal and abnormal lung sounds to help you train your ear. Mentorship from experienced clinicians can provide valuable feedback and guidance on your technique. Medical schools often offer simulation labs where students can practice auscultation in a controlled environment. Consistent practice and continuous learning are key to mastering the art of chest auscultation.
11. What Role Does Technology Play in Modern Chest Auscultation?
Technology enhances modern chest auscultation. Digital stethoscopes and sound analysis software improve accuracy and convenience.
Answer: Technology plays a significant role in modern chest auscultation through digital stethoscopes and sound analysis software. Digital stethoscopes amplify sounds, filter out background noise, and record lung sounds for later review. Sound analysis software can help identify subtle abnormalities that might be missed with traditional auscultation. According to a study in the “Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare,” digital stethoscopes can improve the accuracy of remote auscultation, making them useful in telemedicine applications. These technologies enhance diagnostic capabilities and provide convenient tools for monitoring respiratory health.
12. How Does Streetsounds.net Support Learning About Chest Sounds?
Streetsounds.net offers resources for learning about chest sounds. From sound libraries to expert articles, find everything you need.
Answer: Streetsounds.net supports learning about chest sounds by providing a comprehensive library of audio examples, detailed articles, and expert insights into respiratory health. Our website features recordings of normal and abnormal lung sounds, allowing you to train your ear and improve your diagnostic skills. We also offer articles written by experienced healthcare professionals, covering topics such as auscultation techniques, common respiratory conditions, and the latest advancements in diagnostic technology. Streetsounds.net serves as a valuable resource for anyone looking to enhance their understanding of chest sounds and respiratory health.
13. What is the Significance of Chest Auscultation in Diagnosing Pneumonia?
Chest auscultation plays a crucial role in diagnosing pneumonia. Recognizing specific sounds aids early detection and treatment.
Answer: In diagnosing pneumonia, chest auscultation is significant because it can reveal characteristic crackles (rales) and bronchial breath sounds over the affected lung area. Crackles are caused by the opening of collapsed alveoli due to inflammation and fluid, while bronchial breath sounds indicate consolidation. A study in the “New England Journal of Medicine” highlights that auscultation findings, combined with clinical signs like fever and cough, can help differentiate pneumonia from other respiratory conditions. Early detection through auscultation allows for timely initiation of antibiotic therapy, improving patient outcomes and reducing complications. Chest auscultation remains a cornerstone in pneumonia diagnosis.
14. How Does Chest Auscultation Aid in the Management of Asthma?
Chest auscultation is valuable in managing asthma. It helps assess airway narrowing and response to treatment.
Answer: Chest auscultation aids in asthma management by detecting wheezing, a high-pitched whistling sound caused by narrowed airways. The presence and intensity of wheezing can help assess the severity of an asthma exacerbation. Monitoring changes in lung sounds after bronchodilator administration helps evaluate treatment effectiveness. The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) guidelines recommend regular auscultation as part of asthma assessment. Detecting decreased wheezing or improved airflow indicates a positive response to therapy, guiding further management decisions. Chest auscultation provides real-time feedback on airway obstruction.
15. Can Chest Auscultation Help in Detecting Heart Failure?
Chest auscultation can assist in detecting heart failure. Specific lung sounds indicate fluid accumulation in the lungs.
Answer: Chest auscultation can help detect heart failure by identifying crackles (rales) in the lung bases, indicating pulmonary edema, a common sign of heart failure. These crackles result from fluid leaking into the alveoli due to increased pulmonary venous pressure. According to the American Heart Association, auscultation findings, along with other clinical signs like shortness of breath and peripheral edema, can raise suspicion for heart failure. Monitoring the presence and extent of crackles helps assess the severity of heart failure and response to diuretic therapy. Chest auscultation supports early detection and management of heart failure.
16. How Does COPD Affect Chest Sounds and What Should You Listen For?
COPD significantly affects chest sounds. Knowing what to listen for aids diagnosis and management.
Answer: COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) affects chest sounds by causing decreased breath sounds overall, along with possible wheezes and rhonchi. Decreased breath sounds result from reduced airflow due to emphysema and airway obstruction. Wheezes indicate narrowed airways, while rhonchi suggest mucus accumulation. The COPD Foundation emphasizes the importance of auscultation in COPD assessment. Regular monitoring of lung sounds helps assess disease severity, detect exacerbations, and evaluate response to bronchodilators and other treatments. Recognizing these changes aids effective COPD management.
17. What Specific Techniques Can Improve the Accuracy of Chest Auscultation?
Specific techniques enhance chest auscultation accuracy. These practices ensure reliable and precise assessments.
Answer: Specific techniques to improve chest auscultation accuracy include ensuring a quiet environment, using direct skin contact with the stethoscope, instructing the patient to breathe deeply through the mouth, and following a systematic pattern of auscultation. A quiet environment minimizes interference from external noises. Direct skin contact maximizes sound transmission. Deep breathing enhances audibility of lung sounds. A systematic pattern ensures comprehensive coverage of all lung fields. Guidelines from the American College of Physicians recommend these techniques for optimizing auscultation accuracy.
18. How Can You Use Chest Auscultation to Monitor Post-Operative Patients?
Chest auscultation is useful for monitoring post-operative patients. It helps detect complications like pneumonia or atelectasis.
Answer: Chest auscultation is used to monitor post-operative patients by detecting early signs of complications such as pneumonia, atelectasis (collapsed lung), or pulmonary edema. Decreased breath sounds may indicate atelectasis, while crackles suggest pneumonia or fluid overload. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons recommends regular auscultation as part of post-operative care. Early detection of these complications through auscultation allows for timely interventions, such as chest physiotherapy, antibiotics, or diuretics, improving patient outcomes.
19. What is the Role of Chest Auscultation in Pediatric Respiratory Assessment?
Chest auscultation plays a vital role in pediatric respiratory assessment. It aids diagnosis and management of childhood respiratory illnesses.
Answer: Chest auscultation plays a crucial role in pediatric respiratory assessment, helping diagnose and manage common childhood respiratory illnesses like bronchiolitis, croup, and asthma. In bronchiolitis, wheezing and crackles may be present. Croup can cause stridor, a high-pitched sound indicating upper airway obstruction. Regular auscultation helps assess disease severity, monitor response to treatment, and detect complications such as pneumonia. Pediatric respiratory assessment relies heavily on chest auscultation.
20. How Can You Differentiate Between Upper and Lower Airway Sounds?
Distinguishing between upper and lower airway sounds is key. It aids in localizing respiratory problems.
Answer: Upper and lower airway sounds can be differentiated by their location and quality. Upper airway sounds, like stridor, are typically louder and heard over the neck and upper chest, indicating obstruction in the larynx or trachea. Lower airway sounds, such as wheezes and crackles, are generally heard over the chest and back, suggesting issues in the bronchi and lungs. Understanding these differences helps localize respiratory problems.
21. What are the Ethical Considerations When Performing Chest Auscultation?
Ethical considerations are important in chest auscultation. Respect patient privacy and ensure comfort.
Answer: Ethical considerations when performing chest auscultation include respecting patient privacy, obtaining informed consent, ensuring patient comfort, and maintaining professionalism. Patients should be informed about the procedure and its purpose. Adequate draping should be provided to minimize exposure. Healthcare providers should be mindful of cultural and personal sensitivities. Maintaining these ethical standards ensures patient trust and promotes positive healthcare experiences.
22. How Does Environmental Noise Impact Chest Auscultation and What Can Be Done?
Environmental noise significantly impacts chest auscultation. Minimizing noise is crucial for accurate assessment.
Answer: Environmental noise significantly impacts chest auscultation by masking subtle lung sounds, leading to inaccurate assessments. To minimize this, perform auscultation in a quiet room, turn off electronic devices, and ask others to be silent. Using noise-canceling headphones or a stethoscope with noise reduction capabilities can also help. Creating a quiet environment is essential for obtaining reliable auscultation findings.
23. Can Obesity Affect the Accuracy of Chest Auscultation?
Obesity can affect chest auscultation accuracy. Adipose tissue can dampen and distort lung sounds.
Answer: Obesity can affect the accuracy of chest auscultation by attenuating lung sounds due to increased adipose tissue. This can make it more difficult to detect subtle abnormalities. Using a stethoscope with a larger diaphragm and applying firmer pressure can help improve sound transmission. Positioning the patient upright and having them breathe deeply can also enhance auscultation findings. Awareness of this limitation is essential when assessing obese patients.
24. What are the Limitations of Chest Auscultation Compared to Other Diagnostic Tools?
Chest auscultation has limitations. Other tools offer more detailed information.
Answer: Limitations of chest auscultation compared to other diagnostic tools include its subjective nature, dependence on examiner skill, and inability to visualize internal structures. Imaging techniques like chest X-rays and CT scans provide detailed anatomical information. Pulmonary function tests offer objective measures of lung function. Auscultation is a screening tool that may require confirmation with more advanced diagnostics.
25. How Can Telemedicine Utilize Chest Auscultation Effectively?
Telemedicine can utilize chest auscultation effectively. Digital stethoscopes enable remote assessments.
Answer: Telemedicine can utilize chest auscultation effectively through the use of digital stethoscopes that transmit lung sounds remotely. These devices allow healthcare providers to assess patients’ respiratory status from a distance, improving access to care for those in remote or underserved areas. Remote auscultation can help diagnose and manage conditions like asthma, COPD, and pneumonia. Telemedicine enhances healthcare accessibility and efficiency.
26. How Can Medical Schools Better Train Students in Chest Auscultation?
Medical schools can improve chest auscultation training. Structured curricula and simulation tools enhance skills.
Answer: Medical schools can better train students in chest auscultation through structured curricula, hands-on practice with real patients, simulation tools, and feedback from experienced clinicians. Integrating auscultation training throughout the curriculum and providing opportunities for repeated practice can improve proficiency. Simulation models allow students to practice identifying various lung sounds in a controlled environment. This can enhance auscultation skills.
27. What Innovations are on the Horizon for Chest Auscultation?
Innovations are emerging for chest auscultation. AI and machine learning promise improved diagnostic accuracy.
Answer: Innovations on the horizon for chest auscultation include the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to analyze lung sounds and improve diagnostic accuracy. AI algorithms can detect subtle patterns that may be missed by human ears, aiding in early diagnosis of respiratory diseases. Wearable sensors and smart stethoscopes are also being developed for continuous monitoring of lung sounds. These advancements promise to revolutionize respiratory care.
28. How Can Streetsounds.net Help Me Stay Updated on the Latest in Chest Auscultation?
Streetsounds.net keeps you updated. Expert articles, audio examples, and resources keep you informed.
Answer: Streetsounds.net helps you stay updated on the latest in chest auscultation by providing expert articles, audio examples, and resources on the most recent techniques, technologies, and research findings. Our website features regular updates on innovations in respiratory diagnostics and treatment. Streetsounds.net serves as a comprehensive hub for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
29. What Are the Differences in Chest Auscultation Techniques for Adults vs. Children?
Chest auscultation techniques differ for adults and children. Anatomical and physiological differences necessitate adjustments.
Answer: Differences in chest auscultation techniques for adults and children include stethoscope size, auscultation locations, and patient cooperation. Smaller stethoscopes are used for children to fit their chest size. Auscultation locations may vary due to anatomical differences. Children may require distraction techniques to ensure cooperation. Pediatric auscultation requires patience and adaptation.
30. How Does Body Position Affect Chest Sounds During Auscultation?
Body position affects chest sounds during auscultation. Different positions alter lung volumes and airflow.
Answer: Body position affects chest sounds during auscultation by altering lung volumes and airflow patterns. Sitting upright allows for optimal lung expansion, while lying down can cause compression of the lower lobes. Auscultating in multiple positions can help detect subtle abnormalities.
31. What Are the Key Terms to Know for Describing Chest Sounds?
Key terms describe chest sounds. These terms ensure clear communication and accurate documentation.
Answer: Key terms for describing chest sounds include breath sounds (normal, decreased, absent), adventitious sounds (wheezes, crackles, rhonchi, stridor), intensity (loud, soft), pitch (high, low), and location (upper lobe, lower lobe). Using these terms ensures clear and accurate communication among healthcare professionals.
32. How Can I Use Streetsounds.net’s Audio Library to Improve My Skills?
Use Streetsounds.net’s audio library to hone skills. Listen to various sounds and compare them.
Answer: You can use Streetsounds.net’s audio library to improve your skills by listening to a wide range of normal and abnormal lung sounds. Compare and contrast different sounds, such as wheezes, crackles, and rhonchi, to develop your ability to distinguish between them. Use the audio library as a training tool.
33. What Resources Does Streetsounds.net Offer for Advanced Auscultation Techniques?
Streetsounds.net offers advanced resources. Articles, expert interviews, and detailed guides enhance expertise.
Answer: Streetsounds.net offers advanced resources for auscultation techniques, including detailed articles, expert interviews, and comprehensive guides. These materials provide in-depth knowledge for experienced professionals seeking to refine their skills and stay updated on the latest advancements in respiratory assessment.
34. How Does Streetsounds.net Support Medical Education Programs?
Streetsounds.net supports medical education. Audio libraries, articles, and resources supplement curricula.
Answer: Streetsounds.net supports medical education programs by providing a comprehensive library of audio examples, detailed articles, and resources that supplement traditional curricula. Medical schools can utilize our materials to enhance auscultation training for students.
35. What Steps Should I Take if I Detect Abnormal Chest Sounds?
Detecting abnormal chest sounds requires action. Document findings, consult with colleagues, and order tests.
Answer: If you detect abnormal chest sounds, document your findings, consult with colleagues, and consider ordering additional diagnostic tests such as chest X-rays or pulmonary function tests. Timely intervention can improve patient outcomes.
36. How Does Airflow Obstruction Manifest in Chest Auscultation?
Airflow obstruction manifests in chest auscultation. Decreased breath sounds and wheezing are common signs.
Answer: Airflow obstruction manifests in chest auscultation as decreased breath sounds, prolonged expiratory phase, and wheezing. These findings suggest narrowed airways.
37. What Specific Skills Are Needed to Auscultate Pediatric Patients Effectively?
Skills are needed for pediatric auscultation. Patience, communication, and specialized techniques are essential.
Answer: Specific skills needed to auscultate pediatric patients effectively include patience, good communication skills, and knowledge of pediatric-specific auscultation techniques. Building rapport with children is crucial.
38. How Can I Integrate Chest Auscultation Into a Holistic Patient Assessment?
Integrate chest auscultation into assessments. Combine findings with history, exam, and tests.
Answer: Integrate chest auscultation into a holistic patient assessment by combining your findings with the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and other diagnostic tests. This comprehensive approach enhances diagnostic accuracy.
39. What Are the Legal Implications of Misinterpreting Chest Sounds?
Misinterpreting chest sounds has legal implications. Accurate assessment is crucial for patient safety.
Answer: Misinterpreting chest sounds can have legal implications, particularly if it leads to delayed or incorrect diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare providers have a responsibility to provide competent care.
40. How Does Streetsounds.net’s Community Forum Support My Learning?
Streetsounds.net’s forum supports learning. Connect with peers, share experiences, and ask questions.
Answer: Streetsounds.net’s community forum supports your learning by providing a platform to connect with peers, share experiences, ask questions, and receive feedback from experienced professionals. This collaborative environment enhances your understanding and skills.
By understanding how to listen to chest sounds, you are equipping yourself with a vital tool for assessing respiratory health. Whether you are a healthcare professional or someone keen to understand more about the human body, the knowledge and skills gained are invaluable. Remember, consistent practice and continuous learning are key to mastering this art.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of chest sounds? Visit streetsounds.net today to explore our extensive audio library, read expert articles, and connect with a community of like-minded individuals. Enhance your skills, expand your knowledge, and become a confident and proficient listener of chest sounds. Don’t wait—start your journey now!
Address: 726 Broadway, New York, NY 10003, United States.
Phone: +1 (212) 998-8550.
Website: streetsounds.net.
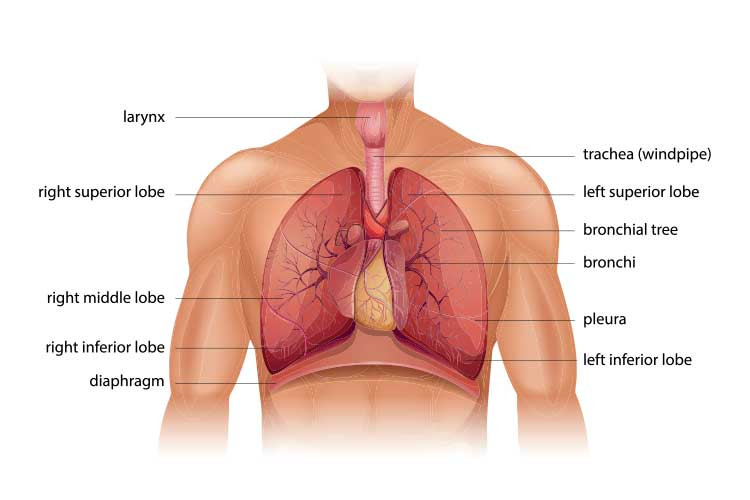 chest auscultation lung diagramDiagram illustrates where vesicular sounds are typically heard, highlighting the lung lobes and showing air movement through the trachea and bronchi.
chest auscultation lung diagramDiagram illustrates where vesicular sounds are typically heard, highlighting the lung lobes and showing air movement through the trachea and bronchi.
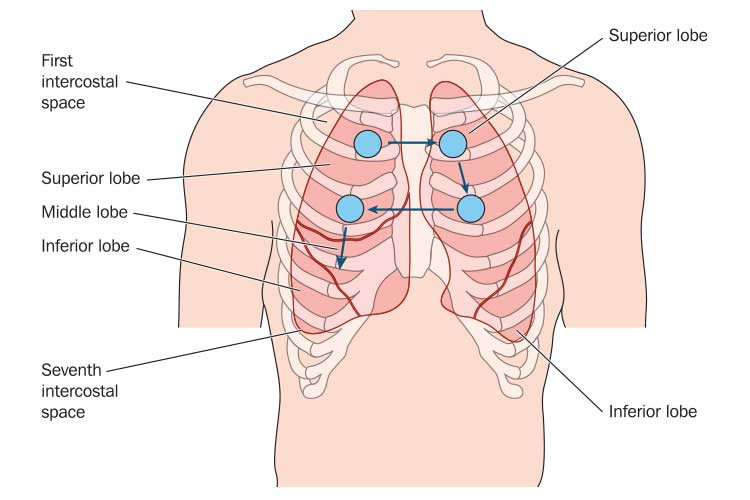 chest auscultation stepladderImage showcases the “stepladder” pattern to systematically listen to lung sounds, ensuring complete coverage of the anterior chest.
chest auscultation stepladderImage showcases the “stepladder” pattern to systematically listen to lung sounds, ensuring complete coverage of the anterior chest.
